-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

MCV Blood Test
The term "Mean Corpuscular Volume," or "MCV," refers to the measurement of the red blood cell's usual size. For assessing and keeping track of general health, an MCV blood test is a crucial testing method. This test is included in a common blood test called a CBC (Complete Blood Count).
What is an MCV Test?
A medical professional can use certain markers to measure the various properties of red blood cells. MCV, or mean corpuscular volume, denotes the typical volume and size of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. MCV blood test high levels may be indicative of a condition such as liver disease or vitamin deficiency. Low levels of MCV are typically associated with anaemia caused by iron deficiency.
Purpose of the MCV Blood Test
MCV test means to measure the following conditions:
- To assess probable anaemia symptoms such as tiredness, pale complexion, and lightheadedness.
- To assess other blood abnormalities, such as an abnormal white blood cell or platelet count.
- To distinguish between different forms of anaemia.
- In people who have certain medical conditions as a prognosis estimate
- As an extra test for many medical problems
How is an MCV Done?
A blood sample extracted from the patient's arm is taken for the test, and it is then sent to a lab for evaluation. The patient's injection site will be cleaned with an alcohol wipe by a medical professional. To prevent blood flow so that the vein may be seen more easily, they will attach a rubber band above the spot. The medical professional will take out the needle after the extraction of the required blood volume.
The blood sample will be carefully examined under a microscope by a lab technician, who will note details about the blood cells, including the typical size of the red blood cells. There is no need for specific preparation required for this test because it is a part of a standard CBC test. It only takes a few minutes to complete the process. To stop the bleeding at the injection site, the medical professional will bandage it and use a cotton ball. The patient should be permitted to leave straight away if no symptoms, such as dizziness, are present.
What Do High MCV Levels Mean?
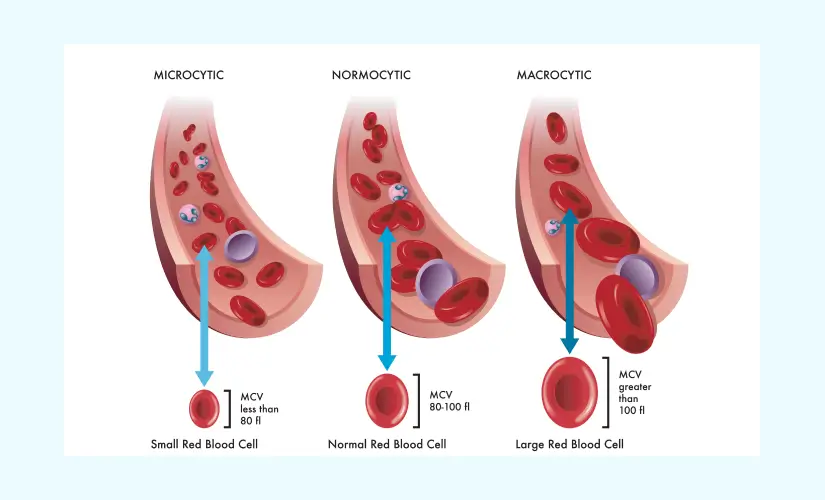
A blood test that shows a high MCV level (more than 100 fl) denotes macrocytic anaemia and shows that the person has larger-than-normal RBCs. The range for a typical/normal MCV blood test is 80 to 100 femtoliters (fl).
The following factors may contribute to elevated MCV levels:
- Vitamin B12 or B9 Deficiency - RBC abnormalities and size imbalances are brought on by Vitamin B12 and B9 deficiency.
- Autoimmune Gastritis - Inflammation of the stomach's body and upper portion is an indication of the chronic condition known as autoimmune gastritis. Folate deficiency results from the progression of this disorder, and this results in macrocytic anaemia.
- Liver Disease - RBCs' cellular composition and structure can be altered by liver illness. For instance, increased cholesterol deposition in RBCs, which affects cell size, is more probable in those with liver illness.
- Chronic Alcoholism - The bone marrow, which is where red blood cells are made, is impaired by alcohol addiction. Due to low RBC counts or exceptionally big RBCs, the MCV level might increase.
- Hypothyroidism - The generation of RBCs is induced by thyroid hormones. So, hypothyroid patients run the danger of developing anaemia.
When Does the Doctor Recommend MCV Test?
When anaemia symptoms, particularly those of macrocytic and microcytic anaemia, arise, the medical professional commonly advises doing the MCV blood test. These signs include-
- Breathing difficulty
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability
- Heartbeat irregularity (arrhythmia)
- Weakness or fatigue
- Extreme numbness and tingling
- Having trouble focusing
MCV Results
Red blood cell size and volume are measured using an MCV test. The MCV test normal range is between 80 fl and 100 fl. A person is more prone to acquire or already have microcytic anaemia if their MCV level is lower than 80 fl. In contrast, they could develop macrocytic anaemia if their MCV levels are higher than 100 fl.
|
|
12-18 years |
Adults |
|
Female |
90 fl |
90 fl |
|
Male |
88 fl |
90 fl |
What is the Normal Range for MCV Levels?
Depending on an individual's age, gender, and the diagnostic lab testing technique utilised the MCV blood test normal range in a blood sample may change.
|
S. No. |
Age |
Gender |
MCV Level |
|
1 |
Children (6 – 12 years) |
Male |
86 fl |
|
|
|
Female |
86 fl |
|
2 |
12 – 18 years |
Male |
88 fl |
|
|
|
Female |
90 fl |
|
3 |
Adults (> 18 years) |
Male |
90 fl |
|
|
|
Female |
90 fl |
What should I do if I Have High MCV Levels?
The best course of action for high MCV is to address the underlying cause of the problem. For instance, dietary changes and supplements may be sufficient if the problem is a folate shortage. The same holds true for long-term alcoholism. In contrast, if an underlying disease is the cause of the increased MCV, the medical professional will create a treatment plan specific to the illness.
Conclusion
The MCV test determines the size and volume of red blood cells. It is not commonly considered a single measurement, but rather as a comparison of results from other RBC and CBCs values. In order to avoid problems in the future, it is crucial to diagnose and treat MCV levels as soon as possible.
CARE Hospitals provide cost-effective access to MCV testing and other laboratory tests, with simple process and rapid turnaround times for results.
FAQs
1. What is the main reason for high MCV?
Ans. The most frequent cause of increased MCV continues to be folic acid and vitamin B12 insufficiency. Certain medications might also result in increased MCV levels.
2. How long does it take for the MCV to stabilise?
Ans. It takes roughly a month to complete therapy for a vitamin B12 deficiency. If drinking is the cause, it will go back to normal if the person quits.
3. What risks may this test pose?
Ans. There is no risk associated with MCV blood testing. There could be some mild bruising and discomfort where the needle entered the arm, but these symptoms normally go away quickly.
4. What does having an MCV low in blood test mean?
Ans. Iron deficiency and microcytic anaemia are conditions that are both indicated by low MCV levels in the blood test.
Reference:https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/mcv-levels#definition
https://www.verywellhealth.com/mean-corpuscular-volume-overview-4583160
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/24641-mcv-blood-test
https://www.medicinenet.com/what_does_it_mean_if_your_mcv_is_high/article.htm
Still Have a Question?



