-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Shoulder Bursitis
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Shoulder Bursitis (Rotator Cuff Bursitis)
Shoulder bursitis (or rotator cuff bursitis) is a major cause of shoulder pain that affects people across all age groups. The rotator cuff has four key muscles that work collectively to control shoulder movement: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis (SITS). Shoulder bursitis happens when small sacs filled with fluid, or bursae, that cushion your shoulder joint swell up and get inflamed. This article explains what shoulder bursitis is and its causes, treatments, and prevention strategies.
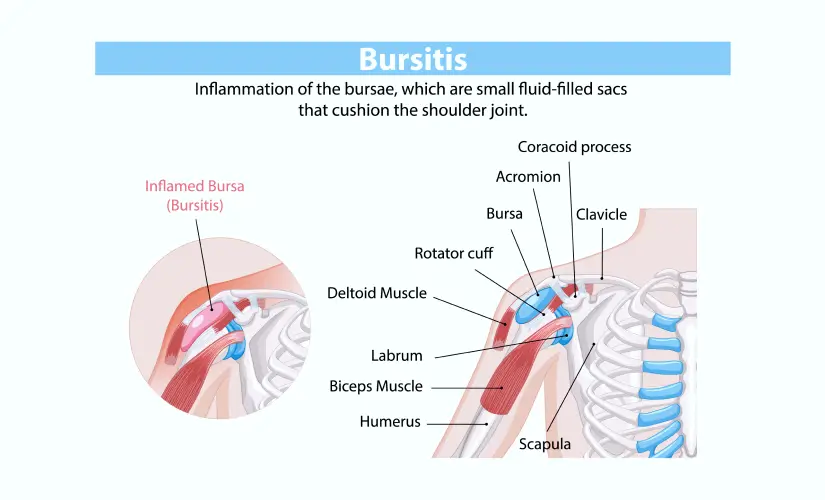
What is Bursitis of the Shoulder?
Your shoulder has little sacs filled with fluid called bursae. They act as cushions between your bones, muscles, and tendons. These tiny pillows help your shoulder joint move smoothly by reducing friction.
The medical term "subacromial bursitis" describes what happens when your shoulder's bursa becomes inflamed. This condition develops in the subacromial bursa that sits between your rotator cuff tendons and the acromion (the highest point of your shoulder blade). Your bursa swells up to create extra cushioning when there's too much friction. This swelling creates a painful cycle by narrowing the space in your shoulder and causing more irritation.
Shoulder Bursitis Symptoms
Common symptoms are:
- A dull, aching pain in the shoulder
- Sharp or pinching pain during overhead arm movements
- Pain that gets worse with activity
- Tender spots around the shoulder
- Limited movement and stiffness
- Swelling and warmth in the affected area
Most patients feel increased pain between 60° and 120° of shoulder movement—known as the "painful arc of motion." The discomfort tends to be worse at night, particularly when you sleep on the affected shoulder.
Causes of Shoulder Bursitis
The following are some common causes of shoulder bursitis:
- Regular overhead activities like painting, swimming or tennis
- Falls or accidents causing direct injury
- Shoulder impingement syndrome
- Bacterial infections
- Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
Risk Factors of Shoulder Bursitis
Some people have a higher chance of developing this condition, such as
- Athletes who do overhead movements
- People whose jobs involve shoulder work (painters, carpenters, gardeners)
- Those with inflammatory conditions like gout or rheumatoid arthritis
- People who have diabetes, kidney disease, or thyroid disorders
- Adults over 40 due to natural tendon wear and tear
Complications of Shoulder Bursitis
Untreated shoulder bursitis might cause:
- Lasting damage to the bursae
- Limited shoulder movement
- Higher risk of rotator cuff tears
- Infection spread (in septic bursitis)
- Sepsis (rare)
Diagnosis of Shoulder Bursitis
- Physical examination: Doctors look for tender spots and swelling and test how well you can move your shoulder. Your doctor will press different areas around your shoulder joint to find the exact bursa that hurts. The physical exam usually shows limited movement. Pain peaks when you raise your arm sideways between 70-120 degrees.
- Your doctor might recommend these tests:
- Imaging tests—X-rays don't show bursitis directly but rule out other issues like arthritis or bone spurs. Ultrasounds and MRIs show soft tissues better and reveal bursa inflammation.
- Laboratory tests—Blood tests or bursa fluid analysis—help determine if an infection or condition like rheumatoid arthritis causes the inflammation.
Shoulder Bursitis Treatment
Your shoulder bursitis should get better with basic treatment methods:
- Rest and activity modification - Your shoulder needs time to heal. Avoid overhead activities or sports that temporarily aggravate your shoulder.
- Ice therapy - Ice packs for 15-20 minutes several times a day reduce inflammation. Put a thin towel between the ice and your skin.
- Medications - Over-the-counter pain relievers help with pain and swelling. Your doctor might give you stronger medications for severe cases.
- Corticosteroid injections - These shots directly into the bursa are a great way to get relief from inflammation when other treatments don't work.
- Physical therapy - Specific exercises make your shoulder muscles stronger and more flexible. This helps recovery and stops future problems.
- Surgery - Doctors recommend surgery when other treatments do not provide sufficient relief. Surgery might remove the inflamed bursa or fix bone spurs that cause irritation.
Low-Dose Radiation Therapy (LDRT) for Shoulder Bursitis
LDRT is a non-surgical and completely painless approach that gives you relief from long-lasting shoulder bursitis; your doctor may go for Low-Dose Radiation Therapy in chronic joint pain and inflammatory cases. With the help of low doses of targeted radiation, it reduces chronic inflammation and pain in the affected bursa. LDRT modulates the immune response and decreases the inflammatory cells causing swelling and discomfort. The therapy is usually delivered over a few short sessions and is well tolerated, offering long-term relief without the need for surgery or repeated steroid injections.
When to See a Doctor
You should call your doctor if you notice:
- Shoulder pain that stays after two weeks of home treatment
- Sharp or sudden pain that affects your daily life
- You can't move your arm
- Your shoulder looks deformed or very swollen
- You have fever, redness, or warmth near the joint (these might show infection)
- Pain spreads from your chest to your jaw, arm, or neck (this could mean heart problems)
Prevention of Shoulder Bursitis
Preventing shoulder bursitis is nowhere near as difficult as treating it once you have it. You can avoid painful inflammation by taking action now.
You can keep your shoulders safe by adopting these habits (including but not limited to):
- Warm up well before you do any exercise
- Maintain correct shoulder posture
- Build stronger shoulder muscles with gentle exercises using light weights or resistance bands
- Take breaks often when you do the same movement over and over
- Don't push through pain - stop what you are doing right away
- Wear protective gear for risky activities
- Lift things the right way - keep your back straight, bend your knees, avoid lifting above your head
- Eat foods that fight inflammation like fish, nuts and leafy greens
- Keep your stress levels down with relaxation methods
Note that paying attention to what your body tells you is the best way to prevent injury.
Conclusion
Shoulder bursitis makes simple daily tasks painful and challenging. Knowledge about this condition gives you the ability to manage your health better. Pain during arm movements, tenderness, and limited mobility are key warning signs that help you identify problems early. Most people achieve full recovery through simple approaches like rest, ice therapy, and gentle exercises.
Prevention works better than recovery. Basic habits protect your shoulders—proper warm-ups, good posture, and regular breaks during repetitive tasks. Healthy shoulders let us hug our loved ones, reach for objects, and enjoy sports without worry. Taking care of these complex joints protects both your physical abilities and quality of life. Don't wait to see a doctor if you have ongoing shoulder pain—your future self will thank you for dealing with it now rather than later.
FAQs
1. How long does a shoulder bursa take to heal?
A mild case of shoulder bursitis usually gets better within 2-4 weeks with proper home care. Recovery takes 6-8 weeks for moderate cases that need therapy or injections. Patients with severe or chronic cases might need 3-6 months to recover, especially after surgery. The healing time depends on the cause—bursitis from injuries heals faster than cases from repeated use.
2. What not to do with shoulder bursitis?
These activities can make your symptoms worse:
- Reaching or throwing objects overhead
- Movements that put stress on your rotator cuff through heavy lifting
- Triceps dips
- "Playing through pain" when you should rest
3. What is the main cause of shoulder bursitis?
Your shoulder can develop bursitis from repeated movements and overuse. The condition also stems from sports injuries, falls, or direct trauma. People in certain jobs face higher risks—carpenters, painters, musicians, and athletes.
4. What is immediate relief for shoulder bursitis?
These steps can help ease your pain:
- Rest your shoulder
- Apply ice for 15-20 minutes several times each day
- Take over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications
- Wrap your shoulder with an elastic bandage

Still Have a Question?

