-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Bleeding Gums
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding from the gums, medically known as gingival bleeding, can be an alarming symptom. This article provides a detailed overview of bleeding gums - their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, home remedies, and when to consult a doctor.
What Are Bleeding Gums?
Bleeding gums refer to bleeding from the gums, typically while brushing teeth, flossing, or eating crunchy foods. It is the cardinal symptom of gum diseases like gingivitis (mild gum inflammation) and periodontitis (advanced gum infection). Bleeding can also result from aggressive brushing, ill-fitting dentures, hormone changes, diabetes, leukaemia, blood thinners, and vitamin deficiency.
Mild and infrequent gum bleeding is usually not a major concern. But frequent bleeding gums and gums bleeding for no reason indicate an underlying dental/health issue needing treatment.
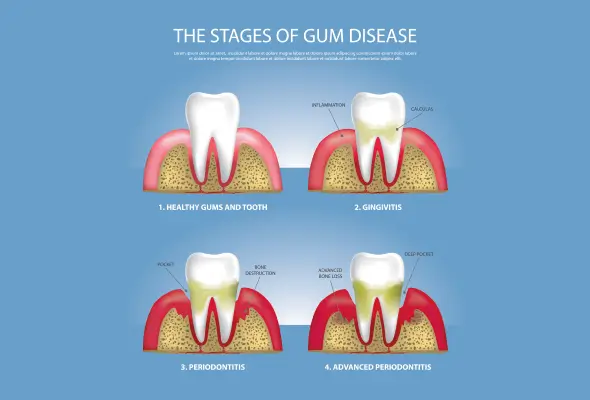
Symptoms of Bleeding Gums
Some symptoms of bleeding gums are as follows:
- Gums bleeding when brushing or flossing your teeth. This is one of the most common symptoms of gum issues.
- Gums appear red, swollen, and tender to touch.
- Receding gums is a symptom where gums pull back from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth surface. This can increase sensitivity.
- Advanced gum disease may cause teeth to become loose or unstable in their sockets. This occurs as the disease damages the tissues supporting the teeth.
- You may experience a metallic taste in your mouth, which is an unpleasant symptom.
- Inflamed gums that bleed often look shiny, smooth, and bright red due to increased blood flow to the area.
- Gums affected by disease may feel soft, swollen, and spongy.
- Receding gums between teeth, known as black triangle disease, can signify gum loss.
- Pus discharge is a symptom of advanced infection causing abscess in the gums.
- Tooth alignment may shift as the disease progresses, causing teeth to drift out of position.
- Tooth sensitivity may increase as gums recede, exposing sensitive tooth roots.
Causes of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can result from various gum diseases, oral health issues, and underlying medical conditions. Let's look at the potential causes in detail:
- Plaque Buildup: Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria, food debris, and saliva on teeth. When not removed by brushing/flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, which irritates gums and makes them prone to bleeding.
- Gingivitis: Early reversible form of gum disease caused by plaque buildup. It causes red, swollen, and tender gums that bleed easily, even with gentle brushing.
- Periodontitis: Advanced irreversible gum infection that damages gums and jawbone, leading to loose teeth that may fall out. This is a major cause of bleeding gums.
- Aggressive brushing: Vigorous brushing with a hard-bristled toothbrush can cause gum abrasions and bleeding.
- Ill-fitting dentures: Improperly fitted dentures may rub against gums, causing irritation and bleeding.
- Oral surgery: Procedures like tooth extraction can temporarily cause bleeding gums.
- Hormonal changes: Puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can cause gums to become sensitive and likely to bleed due to increased blood circulation.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can weaken gums and capillaries, causing them to bleed easily.
- Blood disorders: Leukaemia, haemophilia, and platelet disorders may lead to excessive bleeding from gums.
- Medications: Blood thinners like warfarin, aspirin, and heparin can increase bleeding risks.
- Vitamin deficiency: Vitamin C and K deficiency can cause weak gums prone to bleeding.
- HIV/AIDS: The infection may cause inflammation and ulceration of gums, leading to bleeding.
- Cancer treatments: Chemotherapy and radiation can cause poor immunity and gum problems.
- Eating disorders: Anorexia and Bulimia can lead to deficiencies that can make the gums bleed.
Several dental diseases, oral health factors, and medical conditions can lead to bleeding gums. Seeing a dentist can help determine the exact cause and plan appropriate treatment.
Which medical conditions may cause bleeding gums?
Recognizing the exact cause of bleeding gums can be challenging, but it's important to rule out underlying medical conditions. Here are some disorders that may require immediate medical attention and can lead to bleeding gums:
- HIV Infection: HIV weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including dental issues like bleeding gums. This condition is confirmed through blood tests.
- Anemia: This condition results from a lack of red blood cells. Pernicious anemia, which is linked to Vitamin B12 absorption issues, can also cause bleeding gums.
- Herpes Infection: The herpes simplex virus can lead to pain and soreness in the mouth, which may include bleeding gums.
- Stress: High-stress levels can cause gum inflammation, making them more prone to bleeding. Stress can also weaken the immune system and affect blood clotting.
- Leukemia and Oral Cancer: Oral cancer may appear as painless sores on the gums, cheeks, or tongue and can be accompanied by gum bleeding.
- Factor V Deficiency: This bleeding disorder leads to symptoms like bleeding gums, bruising, and frequent nosebleeds.
- Vitamin deficiency: Vitamin C and K deficiency can cause weak gums prone to bleeding.
- Eating disorders: Anorexia and Bulimia can lead to deficiencies that can make the gums bleed.
Which dental diseases can cause bleeding gums?
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is gum inflammation that often causes bleeding gums. It's treatable if caught early and preventable with good oral hygiene. Risk factors include smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes (especially in women), and dry mouth.
- Periodontitis: Periodontitis, which can develop from untreated gingivitis, also causes bleeding gums. This condition leads to the loosening of gums around the teeth, resulting in bleeding.
- Bleeding Gums During Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause gum inflammation and soreness, leading to bleeding gums. Maintaining good oral hygiene can help, but it's important to see a dentist if the condition worsens.
- Ill-fitting dentures: Improperly fitted dentures may rub against gums, causing irritation and bleeding.
- Oral surgery: Procedures like tooth extraction can temporarily cause bleeding gums.
- Plaque Buildup: Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria, food debris, and saliva on teeth. When not removed by brushing/flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, which irritates gums and makes them prone to bleeding.
Other conditions
Some other bleeding gums can be caused by several factors, including:
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Lack of Vitamin C and Vitamin K.
- Gum Trauma: Injury to the gums.
- Tobacco Products: The use of tobacco can lead to gum bleeding.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause gums to bleed.
- Canker Sores: Small, painful ulcers inside the mouth.
- Brushing and Flossing Techniques: Incorrect methods can damage gums.
- Chemotherapy: Cancer treatment can affect oral health.
- Medications: Certain drugs can cause gums to bleed.
Diagnosis
To diagnose a gum disease, dentists do a thorough checkup. All these tests help dentists correctly diagnose gum diseases and determine their severity. This helps them plan the right treatment. The diagnosis includes:
- Medical history: Dentists ask about symptoms, medications, and health conditions to understand likely causes.
- Dental examination: This involves checking for dental plaque, swollen gums, gum recession, loose teeth, and other signs of gum disease.
- Gum probing: This examination involves testing gum pockets around teeth using a periodontal probe to check for detachment from the tooth.
- Dental X-rays: Doctors assess bone loss around teeth and damage due to gum disease.
- Blood tests: These tests help diagnose blood disorders, vitamin deficiency, diabetes, leukaemia, and other systemic causes.
Treatment
Bleeding gums treatment involves addressing the underlying issue. A few bleeding gum treatment options include:
- Professional cleaning: This procedure involves the removal of plaque and tartar deposits, and smoothing of rough tooth surfaces. It’s typically done every 6 months.
- Scaling and root planing: It is a deep cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar below the gum line and smooth root surfaces.
- Medications: Medications, such as antibacterial mouth rinses, antibiotic gels, or antibiotics, are commonly prescribed for gum infections and bleeding gums.
- Gum treatments: Gum grafts and flap surgery are recommended, depending on the severity of the gum disease.
- Addressing underlying causes: Managing diabetes, adjusting medications, taking supplements for vitamin deficiency, denture adjustments, etc, can also help manage gum bleeds.
When to Visit a Doctor?
Bleeding gums that persist for more than two weeks require prompt dental evaluation, even with improved brushing and flossing. Timely treatment of swollen bleeding gums is essential to prevent complications like tooth loss.
Visiting a dentist quickly when gums bleed for extended periods is crucial. The dentist's expertise facilitates accurate diagnosis and effective early treatment. This prevents progression to more complex issues. Addressing problems early minimises complications and improves outcomes. Here’s how seeking timely treatment for bleeding gums can be helpful:
- Bleeding gums often indicate gum disease, which requires professional care.
- Delaying a dental visit and hoping symptoms resolve on their own allows the condition to worsen.
- Gum disease damages the tissues and bone supporting teeth. Without treatment, severe cases lead to tooth loss.
- Catching gum problems early makes treatment easier.
- Dentists can evaluate persistent bleeding to determine the underlying cause. They can then prescribe appropriate treatment to get the condition under control.
Prevention of Bleeding Gums
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visit your dentist for routine cleanings and check-ups every six months.
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: Choose a soft-bristled brush to avoid irritating your gums.
- Avoid Tobacco Products: Smoking or using tobacco can increase the risk of gum disease.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include plenty of fruits and vegetables, which are rich in vitamins and minerals that promote gum health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help wash away food particles and bacteria.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques, as stress can negatively impact oral health.
- Address Underlying Health Issues: Manage conditions like diabetes or hormonal changes that can affect gum health.
- Use Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Consider using a mouthwash that helps reduce plaque and bacteria.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol: Limit alcohol consumption, which can irritate the gums and lead to bleeding.
Home Remedies for Bleeding Gums
While waiting for your dental appointment, you can take steps at home to find relief from bleeding gums. Some home remedies include:
- Brush gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Floss daily
- Rinse your mouth with warm salt water
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash
Adding more vitamin C and K can also help strengthen your gums. Eat plenty of citrus fruits, leafy greens, broccoli, soybeans, and tomatoes.
Finally, avoid things that irritate the gums, such as:
- Sugary foods
- Smoking
- Dehydration
While home care may help soothe bleeding gums, don't delay seeing a dentist for an evaluation.
When should I see a healthcare provider?
Bleeding gums may resolve on their own, but if the bleeding continues for two weeks, it's important to consult a dentist or primary care physician. They may suggest treatment for the bleeding gums, such as a deep dental cleaning, or address any underlying health issues.
Conclusion
Mild, occasional gum bleeding is normal. However frequent bleeding gums indicate underlying gum disease or health issues needing professional treatment. See a dentist promptly to prevent complications like disease progression and tooth loss. Maintaining gum health is vital for keeping natural teeth intact and avoiding problems like loose teeth, bad breath, and tooth decay.
FAQs
1. How do you stop your gum from bleeding?
Brush and floss gently, rinse with salt water or an antiseptic mouthwash, and apply a cold compress to reduce swelling. See a dentist for persistent bleeding.
2. Which deficiency causes gum bleeding?
A deficiency in vitamin C or vitamin K can cause gums to bleed.
3. What is the best medicine for gum bleeding?
Antiseptic mouthwash, chlorhexidine mouth rinse, and good oral hygiene practices are effective. In some cases, your dentist might prescribe antibiotics if there is an infection.
4. Can gum bleeding be cured?
Yes, with proper oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and professional dental care, gum bleeding can be managed and cured.
5. How long can you go with bleeding gums?
If your gums bleed for more than a week despite good oral hygiene, see a dentist. Persistent bleeding can indicate a more serious condition.
6. What vitamin is needed for bleeding gums?
Vitamin C is crucial for gum health. Vitamin K is also important for blood clotting.
7. Are bleeding gums normal in pregnancy?
Yes, hormonal changes during pregnancy can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding, a condition known as pregnancy gingivitis.
8. Can bleeding gums transmit HIV?
HIV is transmitted through blood, not saliva. However, if both people have open sores or bleeding gums, there is a very small risk. It's best to avoid sharing oral hygiene tools and ensure good oral health.
9. Why do I have bleeding gums with bad breath?
Bleeding gums and bad breath are often signs of gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis). Poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, and infections can cause these symptoms.
10. What is the main cause of bleeding gums?
The main cause is poor oral hygiene leading to plaque buildup and gum disease. Other causes include vitamin deficiencies, hormonal changes, and certain medications.

Still Have a Question?



