-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Breast Lumps
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Breast Lumps
A breast lump is undoubtedly a dangerous condition that might be the first sign of breast cancer. Any swelling in the breast is concerning, regardless of how it appears or feels. Even tumours larger than a half-inch in diameter may be felt by hand. However, it is important to understand that not all breast lumps are cancerous. Breast lumps, especially in younger women, may indicate a benign ailment. If you have a lump in your breast tissue, it is necessary to rule out cancer. If you notice a new lump or if the texture of your breast tissue differs from normal, consult a doctor.
The majority of breast lumps are benign, meaning they are not cancerous. Discovering a breast lump might come as a surprise, but it's crucial to understand that it often doesn't pose a long-term health threat.
Nonetheless, a breast lump could serve as an indicator of cancer. Therefore, it's always a prudent decision to seek medical evaluation when encountering any breast lumps or swelling.
While breasts are commonly associated with women, it's essential to note that breast tissue is present in both men and women. Hormonal fluctuations can influence this tissue, leading to the formation of lumps, which, in some instances, can resolve naturally. Breast lumps can manifest at any age.
Infants may develop breast lumps due to the maternal estrogen they receive during birth, and these typically disappear as the estrogen exits their bodies.
Pre-pubescent girls may experience tender breast lumps, but these usually resolve on their own during puberty. Adolescent boys can also develop breast lumps during puberty, which are typically temporary and tend to disappear within a few months.
What are Breast Lumps?
Breast lumps are tumours or growths in the breast tissue. They can occur in the area surrounding the breast tissue, in the breast tissue, or under the arm. A breast lump may often feel notable or heavy. Breast lumps can vary in size, shape, and texture. They can be as small as a pea or larger. While many breast lumps don't cause pain, others might be painful. There are various medical conditions that can cause non-cancerous breast lumps. However, it is important to have any type of breast lump checked by a doctor.
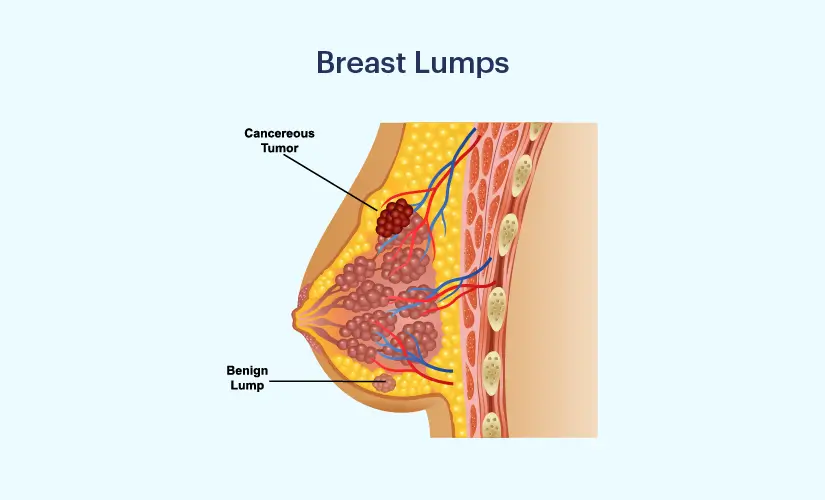
Causes of Breast Lumps
Finding a lump in the breast can be caused by a number of factors. Here are a few common causes of breast lumps:
- Breast alterations caused by fibrocystic changes: A lump may feel like a collection of tiny, fluid-filled sacs and fibrous (rubbery) tissue.
- Breast cysts: Fluid-filled sacs may develop when fluid becomes trapped in milk ducts. Cysts are common in adults who have not gone through menopause.
- Fibroadenomas: These are the most prevalent benign lumps. They often cause little discomfort and commonly affect women aged 20 to 30.
- Phyllodes tumour: A tumour that develops in the connective tissue of the breast.
- Breast infection: Breast tissue infection can lead to a hardened patch of tissue. In a few cases, an infection can cause the development of a solid, distinct lump filled with pus, known as a breast abscess.
- Breast calcifications: Large benign calcium deposits can feel like a hard lump, particularly after a breast reduction or tissue flap treatment.
- Breast cancer: A lump is caused by a tumour growing within the breast tissue.
Symptoms of Breast Lumps
Breast lumps can be detected in either one or both breasts. Breast lump symptoms include:
- An easily movable, round or oval lump that is smooth and may have smooth borders.
- Pain in the nipple area or pulling in of the nipple.
- Clear, yellow, straw-coloured, or dark brown fluid or frank bloody discharge from the nipples.
- Flaky or red nipple or breast skin.
- Breast pain or sensitivity related to the lump.
- The sudden appearance of a large breast lump and increased breast sensitivity just before your period.
- Noticeable improvement in other symptoms after the period, including a smaller breast lump.
- An orange peel appearance on the skin over the breast
Types of breast lumps
Breast lumps can be benign or cancerous and are classified into different types. While benign breast lumps are more common than cancerous ones, it is important to have all types of breast lumps examined by a medical practitioner. The type of breast lumps can be benign or cancerous:
Benign Breast Lumps
Benign breast lumps are non-malignant growths or masses in the breast tissue. They can manifest in various forms and have different causes. Some common types of benign breast lumps include:
- Fibroadenomas
- Fibrocystic Breasts
- Milk Cysts
- Breast Cysts
- Fat Necrosis
- Intraductal Papilloma
- Lipoma
- Mastitis
- Breast Abscess
Cancerous Breast Lump
Cancerous breast lumps are commonly referred to as "malignant tumours." This term is used to describe an abnormal lump of tissue that contains cancerous cells. These lumps may or may not be felt through the skin, and they can vary in size, texture, and discomfort. Breast cancer lumps exhibit similar variations in size, shape, and texture as benign breast lumps. While some breast cancer lumps may feel soft and movable, it is more common for them to feel firm and immovable. Additionally, they may have a more angular rather than smooth feel.
Procedures for diagnosis
Breast lump examinations, imaging tests such as mammograms and ultrasound for breast lumps, and possibly breast biopsies or fine-needle aspirations are commonly used for the diagnosis and testing of breast lumps.
- Breast Exam - The doctor will manually feel the breast with their fingertips. However, additional tests are often required since the doctor cannot determine if a breast lump is a cyst based solely on a clinical breast exam.
- Mammogram and Ultrasound - These imaging scans provide detailed perspectives of the breast. Mammography can often identify large cysts and clusters of small cysts. Ultrasound is used to evaluate whether a breast lump is solid or filled with fluid.
- A needle biopsy- where a needle is inserted into the lump and sent for pathological examination
- Breast lump biopsy- where the larger piece of the lump or the whole lump is sent for pathological examination
If necessary, the doctor may request further breast diagnostic tests to detect breast lumps. If the doctor determines that the lump is benign, the patient can resume routine tests. In cases where a cyst is uncomfortable and tense, the doctor may choose to drain the fluid to provide relief for the patient.
When to see a doctor?
A person should consult a doctor if they observe:
- A breast bulge or a lump beneath the arm.
- The discovery of a new breast lump during a self-examination.
- Changes to the nipple, such as inversion or discharge.
- Presence of bruises on the breast without any known injury.
- Dimpling or puckering of the skin.
Breast Lump Treatment
The treatment for a breast lump depends on its underlying cause. Some lumps may not require treatment, while others may need intervention. The treatment options for breast lumps include:
- Fine-needle aspiration: This procedure involves removing fluid from a breast cyst. If all the fluid is successfully drained, the breast lump will dissolve, and the symptoms will resolve.
- Hormone use: Birth control pills or other hormone treatments may be recommended to manage monthly periods and reduce the recurrence of breast cysts. However, hormone treatments should only be used under the instruction of a healthcare professional due to potential serious adverse effects.
- Breast surgery: Breast lump surgery may be recommended if there is persistent pain in the breast cyst, if the fluid surrounding the cyst is tinged with blood, or if other concerning symptoms are present.
Conclusion
Breast lumps can develop due to a number of causes. They are normal and are not often malignant. Don’t panic if you discover a lump or any other changes in your breast, see a healthcare professional immediately.
FAQs
1. What kinds of lumps are normal in breasts?
It is typical for breast tissue to be lumpy or thick. Breast tissue can change due to breastfeeding and hormonal changes, and a lump does not always indicate cancer.
2. Does a breast lump mean I have cancer?
The most common sign of breast cancer is a lump or tumour in the breast. However, not all breast lumps are cancerous.
3. What kinds of lumps should you worry about?
You should have the lump examined if it is painful, hot or red, firm, and immovable. Contact your doctor if the lump persists for more than two weeks after removal or if it grows back.
4. What does a cancerous breast lump feel like?
A cancerous lump is often firm and not soft or mushy. Additionally, its edges tend to be sharp, uneven, and asymmetrical rather than smooth.
5. Will breast lumps go away on their own?
Some breast lumps may go away on their own. However, it is recommended to consult a doctor right away if you notice a breast lump.
6. Where is breast cancer usually located?
Breast lumps are often seen in the upper outer quadrant of the breast in case of breast cancer. They often appear close to the nipple in males.

Still Have a Question?



