-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Bump on Head
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Bump on Head
A bump on your head can be worrying, but most are harmless and easy to treat. Do these bumps ever trouble you? You may be anxious about these raised areas on your scalp. You can have these after a minor injury or sometimes you get these without any obvious reason.
Head lumps stem from health conditions that range from harmless to serious. Common issues like acne, eczema, or pilar cysts often cause small bumps. A painful bump might be a scalp hematoma—a blood clot that forms after an injury. Hard bumps that change shape and size need immediate medical attention because they could signal skin cancer, though this is rare.
Some itchy bumps on the head under hair go away on their own, while others need a doctor's evaluation. This is particularly true for bumps that appear after an injury or come with swelling, redness, or tenderness. Knowing which bumps need medical care helps people handle these situations better.
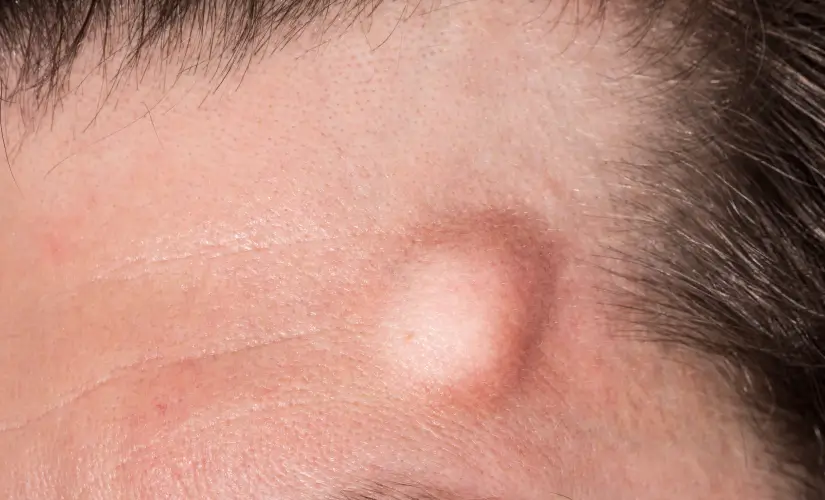
Symptoms of a Bump on the Head
- Bumps on the head that itch can be due to various reasons like acne, hives, folliculitis, or allergic reactions.
- Your head bump usually shows swelling, redness, and feels tender where you got hurt.
- You might notice bruising, warmth, and sometimes drainage.
- More serious signs include headaches, dizziness, confusion, nausea, and vision problems.
- Kids who cry constantly or seem irritable after hitting their head need careful watching.
Causes of Bumps on the Head
- Direct injuries like falls, car accidents, or sports collisions cause most head bumps.
- They can also come from acne, cysts, folliculitis, ingrown hairs, bone spurs, or lipomas.
- Sometimes, sinusitis or tumours can make certain parts of your head swell up.
Risk Factors
- Excess sweating
- Head lice
- Adults over 65
- Kids under 4
- People with physically demanding jobs get head injuries more often.
- Athletes who play contact sports also bump their heads more because they crash and collide frequently.
Complication of a Bump on the Head
Bleeding inside your skull (subdural hematoma) can put pressure on your brain. This might damage your brain temporarily or permanently. Your bump could also get infected, especially if you break the skin.
Diagnosis
If you are going to your doctor for these bumps they will first check the bump physically then test your nerve. Sometimes they might order CT scans or MRIs. You will also have a blood tests to find out any infection or other problems causing the bump.
Head Bump Treatment
- Rest, ice packs in a cloth, and pain relievers work well for minor bumps.
- Stay away from NSAIDs since they might make bleeding worse.
- Serious injuries need hospital stays, monitoring, or surgery.
When to See a Doctor
Rush to the doctor if:
- You throw up
- Get severe headaches
- You feel confused or pass out
- You see clear fluid coming out of your ears or nose
- You have seizures
- You can't speak properly after hitting your head.
Also, get checked if your bump grows bigger, leaks fluid, or keeps hurting after a few days.
Conclusion
People get head bumps at any age and for various reasons. Simple injuries cause most bumps that heal with basic home care. Your body recovers better with rest, ice packs, and common pain relievers like paracetamol.
Some warning signs just need quick medical care. You should never ignore symptoms like vomiting, severe headaches, confusion or clear fluid coming from your ears after an injury. Medical evaluation becomes necessary when bumps grow larger, ooze discharge, or stay painful for several days.
Children's head injuries need extra attention since they might not explain their symptoms well. Older adults face bigger risks from head impacts, so they should get a full picture quickly.
A bump on your head might seem alarming, but understanding the difference between a small swelling and something serious helps you decide what to do. This basic knowledge gives you the ability to choose between self-care and professional help.
Your skull has several natural bumps, particularly where neck muscles connect at the back. Not every bump means trouble. Your health matters, so think over any head trauma carefully. Taking quick action when symptoms worry you protects your health and helps you recover with peace of mind.
FAQs
1. Is a bump on the head always serious?
No. Most head bumps result in minor scalp injuries with swelling or bruising. Small injuries usually heal without complications. Someone should watch for developing symptoms.
2. At what time should I worry about a bump on the head?
Rush to medical care if headaches get worse, vomiting repeats, confusion sets in, memory fades, seizures occur, clear fluid leaks from ears/nose, unconsciousness happens, balance fails, or pupils become unequal. Babies under 1 year need prompt evaluation if they cry excessively.
3. What are the signs of a concussion after hitting your head?
A person with a concussion might experience headaches, confusion, dizziness, nausea, light or noise sensitivity, balance problems, blurred vision, memory issues, and foggy feelings.
4. How long does it take for a bump on the head to go away?
Most bumps heal within a few days to a week. Deep headaches typically clear up within 24 hours. The scalp's pain might last 3 days.
5. Can a head bump cause internal bleeding?
Yes. A blow to the head can cause bleeding between the brain and skull (hematoma). Symptoms might appear right away or develop over hours or days.
6. What are the symptoms of a serious head injury?
Heavy bleeding, blackouts, seizures, vision changes, clear fluid from the ears/nose, slurred speech, limb weakness, trouble staying awake or growing confusion need immediate attention.
7. Can a bump on the head cause a headache?
Absolutely. Head injuries commonly cause headaches that might last for days or weeks. Medical help becomes necessary if headaches worsen or don't improve with rest and pain relief.
8. How do I treat a minor bump on the head at home?
Put ice wrapped in cloth on the area for 20 minutes (never directly on skin), take paracetamol for pain (avoid ibuprofen/aspirin), rest, and let someone check on you for 24 hours.
9. Why does a head bump swell so quickly?
The scalp's rich blood supply explains the rapid swelling. Blood vessels under the skin release blood into nearby tissue when injured.

Still Have a Question?

