-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Psoriasis Symptoms
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Psoriasis Symptoms
Psoriasis is an uncomfortable autoimmune condition that causes itchy, scaly patches of skin called plaques. It mainly occurs in elbows, knees, lower back, and head/scalp. Although there is no cure, certain treatments can be done for symptom management.
Let’s discuss the symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis, and treatment of psoriasis. We will also cover other essential aspects, including - when to see a doctor, risk factors, medical complications, and home remedies.
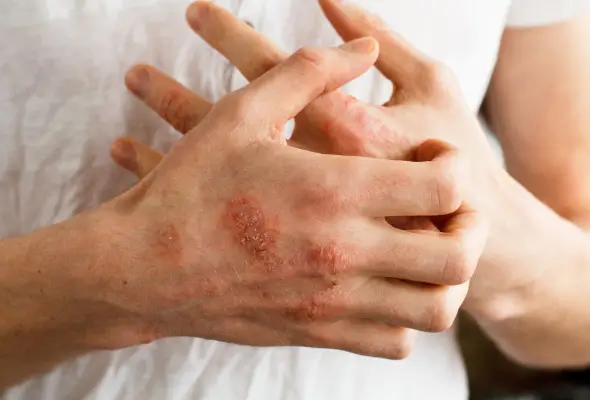
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis causes more than just skin plaques and rashes. People with psoriasis often experience additional symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Being aware of the range of potential psoriasis symptoms can help you identify the need to seek medical care.
Common psoriasis symptoms beyond the visible skin plaques include:
- Itchy skin that may feel intensely uncomfortable, with sensations of burning or stinging. The itchiness can be severe enough to keep you up at night.
- Dry, cracked areas of skin in which even light scratching could lead to bleeding. In the cold season – winter, when there is drier air - the skin can become very susceptible to painful cracking.
- Pitting, discolouration, crumbling and abnormal thickening of fingernails and toenails. Nail psoriasis can be embarrassing and make nail care difficult.
- Aching, tender joints that may throb, swell or feel stiff. Joint pain affects up to 30% of people with psoriasis.
Although the temptation to scratch irritating scales is huge, one has to refrain from scratching in order not to hurt the skin and worsen the condition.
Seek medical attention immediately if you experience severe pain, fever, and swelling, as these can indicate a severe infection. Being attentive to all of your symptoms, not just skin plaques, is key to adequately managing psoriasis and maintaining your quality of life. Discuss lifestyle impacts with your doctor to determine the most effective treatment plan.
Causes of Psoriasis
- Psoriasis happens when the immune system overreacts, causing inflammation. Normally, the immune system fights the bacteria and avoids infections. But with psoriasis, the immune system attacks healthy skin cells by mistake.
- This speeds up the growth cycle of skin cells, causing a buildup of cells that appear as plaques. The speeded-up cell process also leads to shedding and scaling.
- Additionally, since psoriasis has genetic aspects, it means that if you have one of the parents who also suffers from this illness, you are likely going to develop it, too.
Types of Psoriasis
There are different kinds of psoriasis, and each has its own unique symptoms:
- Plaque psoriasis - Most common type; causes dry, raised, scaly patches
- Nail psoriasis - Affects nails, causing pits, abnormal growth, and discolouration
- Guttate psoriasis - Affects young adults/children; causes small, scaling spots
- Inverse psoriasis - Appears in skin folds; causes smooth, inflamed patches
- Pustular psoriasis - Causes pus-filled blisters on palms/soles or widespread
- Erythrodermic psoriasis - Causes severe, peeling rash over large areas
What part of my body will psoriasis affect?
A psoriasis rash can appear anywhere on your skin. It's most commonly found on:
- Elbows and knees
- Face and inside your mouth
- Scalp
- Fingernails and toenails
- Genitals
- Lower back
- Palms and feet
For most people, psoriasis affects just a small area of skin. In more severe cases, the patches can join together and cover a large portion of your body.
Diagnosis
A doctor will diagnose with a visual inspection of the body’s skin for the characteristic, raised, and plaque-shaped lesions.
- The doctor will also inquire about your symptom history, such as when the rashes started appearing and if there is a psoriasis case somewhere in your family.
- Let your doctor know if you have tried any at-home treatments.
- You should also be specific in giving the details on how your signs and symptoms have developed over time because this might facilitate the proper diagnosis.
- Sometimes, the appearance of plaques indicates psoriasis, but your doctor may wish to confirm with a biopsy, especially if symptoms seem unusual.
- During a biopsy, a small sample of skin tissue from a plaque is removed and examined under a microscope, allowing the doctor to rule out other possible skin conditions.
- Being open with your doctor helps them make an accurate psoriasis diagnosis so appropriate treatment can begin.
Treatment
The goal of psoriasis treatment is to reduce symptoms and slow the overproduction of skin cells. Treatment plans are tailored based on factors like age, overall health, and severity of symptoms.
Mild cases may respond well to:
- Moisturizers to reduce dry, itchy skin
- Medicated creams and shampoos applied to the affected areas
- Carefully controlled UV light exposure under a doctor's supervision
More severe psoriasis may require:
- Prescription ointments containing vitamin D, retinoids or steroids
- Oral medications to slow skin cell growth and suppress the immune system's overactive response
- Injections of medications that target overactive immune responses
With moderate to severe psoriasis, combining multiple treatments often provides the best results. Work closely with your doctor to find the most effective treatment plan for your individual case while minimizing side effects. Tracking your symptoms and how well treatments work can help adjust your plan.
Medications
Some over-the-counter remedies might help ease symptoms of mild psoriasis:
- Coal Tar: This can help calm the itching and reduce lesions, especially on the scalp, palms, and soles.
- Hydrocortisone Creams: These can help decrease inflammation and soothe itchy skin.
- Salicylic Acid: Often used for scalp psoriasis, this can help reduce swelling and remove scales.
- Anti-Itch Products: Items containing calamine, hydrocortisone, camphor, or menthol can be useful in relieving itching.
Topical Therapies
A doctor might recommend topical treatments, which are applied directly to the skin. These are usually the first choice for managing mild-to-moderate symptoms, especially in those without psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
- The goals of topical treatments are to:
- Slow down the fast growth of skin cells
- Reduce inflammation
- Relieve itching or discomfort
- Common topical treatments include:
- Corticosteroids, which come in various strengths
- Synthetic vitamin D
- Retinoids, which are forms of synthetic vitamin A
- Pimecrolimus cream and tacrolimus ointment
Systemic Therapies
- Systemic therapies work throughout the whole body to:
- Reduce inflammation
- Slow down the progression of the disease
- Decrease how often flare-ups occur
- Doctors might recommend these treatments to:
- Manage moderate to severe psoriasis
- Address symptoms in sensitive areas like the face, hands, or genitals
- Prevent joint damage in people with psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
When to See a Doctor?
See your doctor if psoriasis:
- Covers large areas or causes significant discomfort
- Doesn't improve with over-the-counter remedies
- Worsens suddenly
Risk Factors
Psoriasis flares can be triggered by:
- Stress
- Skin injuries, cuts or surgery
- Certain medications
- Extreme weather
- Illnesses like strep throat
- Family history
Complications
Psoriasis raises your risk for:
- Stress: High levels of stress can trigger or worsen psoriasis flare-ups. Stress can impact your immune system, leading to increased inflammation and making psoriasis symptoms more severe. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through relaxation techniques, exercise, or therapy, can help keep symptoms in check.
- Skin Injuries, Cuts, or Surgery: Any damage to the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, or even surgery, can lead to a psoriasis flare-up. This is because the healing process can trigger the immune system and cause psoriasis plaques to form in the affected area. It's important to protect your skin and treat any injuries promptly.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can trigger psoriasis or make it worse. These include lithium (used for bipolar disorder), antimalarial drugs, and some beta-blockers (used for high blood pressure). If you’re taking these or other medications, talk to your doctor about potential alternatives or ways to manage side effects.
- Extreme Weather: Both very cold and very hot weather can affect psoriasis. Cold, dry air can lead to dry, cracked skin, which can trigger flare-ups, while hot and humid conditions can cause sweating and irritation. Protecting your skin with moisturizers and appropriate clothing can help minimize these effects.
- Illnesses like Strep Throat: Infections, especially strep throat, can trigger psoriasis in some people. When your body fights an infection, it can worsen psoriasis symptoms or cause new plaques to form. Keeping up with vaccinations and treating infections promptly can help reduce this risk.
- Family History: Psoriasis tends to run in families, so having a family history of the condition can increase your risk. If psoriasis is common in your family, you may be more likely to develop it yourself.
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight can increase inflammation in your body, potentially worsening psoriasis symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help manage and reduce flare-ups.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can both trigger psoriasis or make symptoms worse. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can improve your overall health and potentially reduce psoriasis flare-ups.
Prevention
There are several strategies that can help reduce the risk of psoriasis flare-ups, including:
- Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger symptoms
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Keeping the skin well-moisturized
- Spending time in sunny climates during winter months
- Managing stress through practices like yoga, exercise, and meditation
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake
- Using topical home remedies to soothe itching
Following an anti-inflammatory diet can also be beneficial for managing symptoms and lowering the risk of complications.
Home Remedies to Treat Psoriasis
Natural remedies to try at home include:
- Moisturizing baths with oils, Epsom salts or oatmeal
- Aloe Vera creams
- Omega-3 foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts
- Turmeric/curcumin supplements
- Oregon grape creams
- Humidifiers
- Stress-reduction techniques
- Daily moisturizing
Diet recommendation for people with psoriasis
Eating a healthy diet can help manage your symptoms if you have psoriasis. Here are some dietary tips:
- Eat More Fruits and Vegetables: These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation.
- Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, oatmeal, and whole wheat bread instead of refined grains. They can help keep your digestive system healthy.
- Include Healthy Fats: Add sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (like salmon), flaxseeds, and walnuts. These fats can help reduce inflammation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and help your body flush out toxins.
- Limit Red Meat and Processed Foods: Try to cut back on red meat, processed foods, and sugary snacks, as they can increase inflammation.
- Avoid Foods That Trigger Flare-Ups: Some people find that certain foods, like dairy or gluten, can worsen their symptoms. Pay attention to your body and consider avoiding any foods that seem to trigger flare-ups.
- Moderate Alcohol Intake: Drinking alcohol in moderation or avoiding it altogether can help reduce flare-ups, as alcohol can sometimes trigger psoriasis symptoms.
Living with Psoriasis
- To manage psoriasis effectively:
- Follow your medication instructions.
- Apply moisturizer regularly, especially after showers or baths.
- Avoid using harsh soaps.
- Use medicated shampoo if you have scales on your scalp.
- To stay healthy overall:
- Discuss with your healthcare provider ways to reduce your risk for related conditions like heart disease, depression, and diabetes.
- Reduce stress through meditation, exercise, or talking to a mental health professional.
Conclusion
While chronic, psoriasis is manageable with lifestyle changes and medical treatment. See your doctor if symptoms are interfering with daily life. Staying informed about the condition and available treatments can help you find an effective management plan.
FAQs
1. What part of my body will psoriasis affect?
Ans: Psoriasis can appear anywhere but most often affects the elbows, knees, lower back, scalp, face, and genitals. In mild cases, it's localized, but severe cases can cover large areas.
2. What is psoriatic arthritis?
Ans: About 30% of those with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, causing joint pain, stiffness and swelling. Treating it early on can help prevent permanent joint damage.
3. Does psoriasis affect everyone? Is it very common?
Ans: It is estimated that about 3% of the country’s population suffers from psoriasis. It can develop at any age and affects men and women of all races equally.
4. Is psoriasis painful to touch?
Ans: Yes, psoriasis will lead to aching, burning, and stinging by causing inflammatory nerve irritation of the skin. Flare-ups can be triggered by stress, illness, weather changes, and more.
5: What are the symptoms of starting psoriasis?
Early symptoms of psoriasis often include red, inflamed patches of skin covered with silvery scales. You might also experience itching, dryness, or cracking in the affected areas, which can be painful.
6: Can psoriasis spread?
Psoriasis isn’t contagious, so it doesn’t spread from person to person. However, the condition can worsen or spread to different areas of the body over time, especially without proper treatment.
7: Who gets psoriasis?
Psoriasis can affect anyone, but it’s more common in adults. It often runs in families, so if you have a family member with psoriasis, you might be at higher risk. Factors like stress, infections, and certain medications can trigger it.
8: Can psoriasis be cured?
Psoriasis currently has no cure, but it can be managed with treatments like topical creams, medications, and lifestyle changes. These can help reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
9: Does vitamin D help psoriasis?
Yes, vitamin D can help improve psoriasis symptoms. It slows the growth of skin cells and can reduce inflammation. Topical creams containing vitamin D or getting moderate sun exposure may be beneficial.
10: What deficiency causes psoriasis?
While there isn’t a specific deficiency that causes psoriasis, low levels of vitamin D have been linked to worsening symptoms. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels might help manage the condition.
11: Is sunlight good for psoriasis?
Moderate sunlight exposure can be beneficial for psoriasis because it helps the skin produce vitamin D, which can reduce symptoms. However, too much sun can trigger or worsen symptoms, so it’s important to balance sun exposure.
12: Why do I suddenly get psoriasis?
Psoriasis can suddenly appear due to triggers like stress, infections, skin injuries, or certain medications. If you’re genetically predisposed, these factors can activate the condition.
13: What age does psoriasis start?
Psoriasis can start at any age, but it often begins between the ages of 15 and 35. Some people may develop it earlier or later in life.

Still Have a Question?



