-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation Treatment in Hyderabad, India
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical process in which electrodes are inserted into some parts of the brain. These electrodes commonly known as leads produce electrical impulses that help to control the abnormal activity of the brain. These electrical impulses also normalize the chemical components in the brain which can lead to several conditions.
Stimulation of the brain is controlled by a programmed generator that is positioned in the skin over the upper chest. Doctors can use deep brain stimulation for neuropsychiatric conditions or movement disorders when prescribed medications become less effective or cause side effects and disturb the normal physiology of the patient.
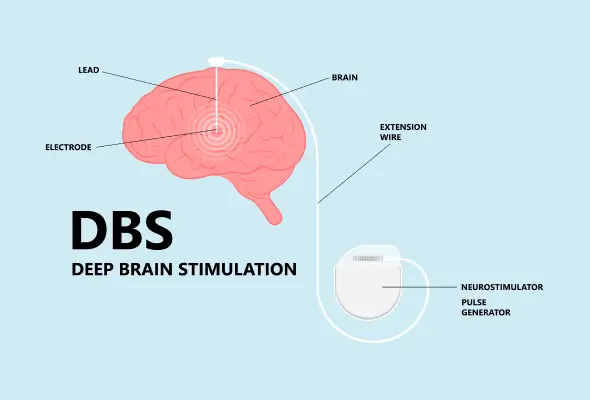
The DBS system consists of three different components.
-
Electrode/lead- It is a thin and insulated wire inserted through a small opening in the skull and placed at specific areas of the brain.
-
Extension wire- It is also an insulating wire that is passed under the skin of the neck, shoulder and head. It connects the electrode to the internal pulse generator (IPG).
-
Internal Pulse Generator (IPG)- It is the third part of the system and is placed under the skin in the upper chest.
How does DBS work?
Movement or locomotion-related disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and other neurological conditions occur due to disorganized electrical signals in certain areas of the brain that control locomotion. When successful, deep brain stimulation interrupts the irregular electrical signals that cause tremors and other movement-related symptoms.
During the process, neurosurgeons implant one or more leads inside the brain. These leads are further connected to an extension wire that establishes a connection between leads/ electrodes to a small neurostimulator (internal pulse generator). After a few weeks of the neurostimulator insertion, the doctor programs it to deliver electrical signals. This programming process may require more than one visit in the week or month to ensure that the neurostimulator is adjusting the current properly and providing effective results. The doctor keeps in mind to establish an optimal balance between reducing the side effects and improving the symptoms while adjusting the device.
Who needs Deep Brain Stimulation?
DBS involves a series of procedures, evaluations and consultations before and after the surgery so that patients who are willing to get this treatment can devote sufficient time to the process. The cost for the DBS process, pre-operative and post-operative follow-up can vary according to the patient’s insurance coverage.
The process can improve movement-related symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and other conditions, but it doesn’t guarantee to provide perfect health for the patient.
Parkinson’s disease
DBS can benefit three types of PD patients-
-
Patients having uncontrolled tremors and medications haven’t provided desired results.
-
Patients experiencing severe motor fluctuations and dyskinesia after withdrawal of drugs.
-
Patients whose movement symptoms respond to higher and more frequent medication doses, but are unable to do so due to side effects.
Essential Tremor
Essential tremor is the most common locomotion disorder. DBS can be an effective treatment for this condition in cases where shaking limits daily activities like shaving, dressing, etc.
Dystonia
Dystonia is an uncommon movement disorder. Its symptoms include twisting movements and abnormal postures. DBS can help to improve the symptoms. However, the response of the patient depends on the cause of the condition, which may be genetic or drug-induced.
What is the process of deep brain stimulation?
There are two methods to conduct DBS. In some cases, the doctor inserts both the neurostimulator and leads in the patient. And in other cases, two surgeries are required separately, to implant the leads and neurostimulator.
Stereotactic DBS and interventional image-guided DBS
In stereotactic DBS surgery, the patient requires to get himself off his medications. During the process, a frame stabilizes the patient’s head and gives coordinates to help the surgeon guide the electrode to the correct positions in the brain. The patient receives local anaesthesia to keep himself comfortable during the entire process along with a mild sedative to keep him relaxed.
In image-guided DBS surgery, the patient is given general anaesthesia and is fall asleep in an MRI or CT scan machine. The surgeon uses MRI and CT images to guide the electrodes to the desired locations in the brain. Generally, this method is recommended for children, patients having extreme symptoms or those who are anxious and fearful. The following is the general procedure for DBS surgery.
Lead Implantation
-
The patient's jewellery, clothing and other objects are removed as they may cause interference during the procedure.
-
The medical team will shave a small part of the head and injects anaesthesia into the scalp so that they can place the head frame.
-
With the help of the screws, the head frame is attached to the skull.
-
The surgical team then uses MRI or CT to point out the target area in the brain where the lead will be attached.
-
After giving some medications, the surgeons make a small hole in the skull to insert the lead.
-
When the lead moves through the brain, the neurosurgeons record the process to check the correct location of the lead.
-
Once the lead is in the correct position, it is then connected to the neurostimulator. Electrical stimulation conducted will help doctors analyse if the symptoms are improved or if any side effects have occurred.
-
An extension wire is attached to the lead connecting the neurostimulator. This wire is placed under the scalp.
-
The hole made in the skull is closed with stitches and a plastic cap.
Microelectrode Recording (MER)
MER (microelectrode recording) uses a current of high frequency to find the accurate surgical area for implanting the DBS (deep brain stimulator). As the structure of each person is different, therefore, the MER gives correct information about the surgical site for placing the DBS. The microelectrode allows the surgeons to hear and see the neuronal activity from different parts of the brain.
Placement of the Neurostimulator
To carry out this process efficiently, the person is given anaesthesia. After this, the medical team inserts the neurostimulator under the outer skin like the collarbone, abdomen or chest. The extension wire is attached to the lead connected to the neurostimulator.
After DBS (Deep Brain Stimulation) Surgery
The Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Surgery in Hyderabad is about 24 hours or longer depending on the recovery of the patient. The doctors will visit the patients at regular intervals and give instructions and advice for home care.
At home, the patient needs to keep their incisions dry and clean. The doctors will provide instructions about how to care for yourself at home after the DBS surgery in Hyderabad. A magnet is given to the patient that can be used to turn off or on the neurostimulator under certain conditions.
Specific Precautions After DBS (Deep Brain Stimulation) Surgery
Patients who had DBS should take the following precautions:
-
Carry an ID card always that states you have a neurostimulator. You can also wear a bracelet that indicates this information.
-
Tell the airport security that you carry a neurostimulator before going through the detector. You should inform the security who have handheld detectors not to use this device for a longer period as the devices may affect the functions of the neurostimulator.
-
Consult the physicians before going through any type of MRI procedure. Also, you should not visit places with large magnetic fields like automobile junkyards or power generators that use large magnets.
-
Do not use heat in physical therapy to cure their muscle problems.
-
Do not use radar or high-voltage machines like smelting furnaces, television transmitters, radar installations or high-tension wires.
-
Inform the surgeons about the neurostimulator before going for other surgery. You should take precautions before and during the surgical process.
-
Protect pacemakers or neurostimulators while performing any physical activity.
Post-Operation Procedures for Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure used to treat a variety of neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. Post-operative care is crucial to ensure the success of the procedure and the well-being of the patient. Here are the key post-operative procedures and considerations:
- Immediate Post-Operative Care
- Hospital Stay: Patients typically stay in the hospital for several days following the surgery for monitoring. This includes neurological assessments to ensure there are no immediate complications such as bleeding or infection.
- Pain Management: Post-operative pain is managed with medications as prescribed by the surgeon. Patients may experience headaches or discomfort at the incision sites.
- Incision Care
- Monitoring for Infection: The surgical sites on the scalp and where the pulse generator is implanted (usually in the chest) must be kept clean and dry to prevent infection. Any signs of redness, swelling, or discharge should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
- Suture Removal: Sutures or staples used to close the incisions are typically removed about 10-14 days after surgery.
- DBS Device Programming
- Initial Programming: The DBS device is usually turned on and programmed a few weeks after surgery once the brain has had time to recover. This is done by a neurologist or a specialist who adjusts the settings to achieve optimal symptom control.
- Follow-Up Adjustments: Multiple follow-up appointments are necessary to fine-tune the settings of the DBS device. The process involves adjusting the electrical impulses to balance symptom relief and minimize side effects.
- Medication Management
- Adjustment of Medications: Patients might need to adjust their medication regimen post-surgery. This is often done gradually and under the supervision of a neurologist to complement the effects of DBS.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Physical Therapy: Some patients may benefit from physical therapy to help regain strength and mobility.
- Occupational Therapy: This can help patients adapt to any changes in their abilities and improve their daily functioning.
- Speech Therapy: If speech issues were present before surgery, speech therapy might be beneficial post-operation.
- Regular Monitoring and Long-Term Care
- Routine Check-Ups: Regular appointments with the healthcare team are essential to monitor the patient's progress and make any necessary adjustments to the DBS device.
- Battery Replacement: The pulse generator's battery will eventually need to be replaced. This is typically done through a minor surgical procedure every 3-5 years, depending on the device and usage.
- Lifestyle
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several weeks post-surgery to allow proper healing.
- Complications and Troubleshooting
- Be Aware of Complications: Potential complications include infection, device malfunction, and stimulation-related side effects like speech or balance issues. Patients should be educated on recognizing these issues and seeking prompt medical attention.
- Device Adjustments: Ongoing communication with the healthcare provider is crucial for addressing any new or persistent symptoms through device adjustments.
Risks of Deep Brain Stimulation
While DBS can be highly effective in managing symptoms of various neurological disorders, it also carries certain risks. Some of the risks associated with Deep Brain Stimulation include:
- Surgical Risks: The implantation procedure involves placing electrodes into specific regions of the brain, which carries risks such as bleeding, infection, stroke, or damage to surrounding brain tissue. These risks are inherent to any surgical procedure and can vary depending on factors such as the patient's overall health and the surgeon's skill.
- Device-related Complications: The implanted device, including the electrodes and pulse generator, may malfunction over time, requiring surgical revision or replacement. This can lead to issues such as device displacement, electrode migration, battery depletion, or hardware failure, necessitating additional surgical procedures.
- Cognitive and Psychological Effects: Some patients may experience changes in cognitive function, mood, or behavior following DBS surgery. These changes can include cognitive decline, memory problems, depression, anxiety, or impulsivity. While these effects are usually mild and reversible, they can sometimes be more severe and impact the quality of life.
- Side Effects of Stimulation: Inappropriate or excessive stimulation of brain regions can result in side effects such as muscle contractions, speech disturbances, tingling sensations, or visual disturbances. Fine-tuning the stimulation parameters is often necessary to minimize these side effects while optimizing symptom control.
- Infection and Device-related Complications: As with any implanted device, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site or around the implanted hardware. Infections can lead to serious complications and may require removal of the device.
How can CARE Hospitals help?
At CARE Hospitals, we follow international treatment protocols to provide comprehensive care and treatment for brain-related disorders. Our well-trained medical team provides assistance and end-to-end care to help patients have a healthy life after the deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery in Hyderabad.
For additional information on the cost of this treatment, click here.
Our Doctors
-
Dr. Sachin Adhikari
MBBS, MS, M.ch (PGI Chandigarh)
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Arpit Agarwal
MBBS, MD (Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Neurology
View More -

Dr. Sanjeev Kumar Gupta
MBBS, MS, MCh
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Sanjeev Gupta
MBBS, MS, MCh
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Abhishek Songara
MBBS, M.S, M.Ch (Neurosurgery )
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Anand Soni
MD, DM (Neurology)
Neurology
View More -

Dr. Ankur Sanghvi
MBBS, MS, Mch (Neuro)
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Arjun Reddy K
MBBS, MS, MCh
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Arun Reddy M
MBBS, DNB – Neurosurgery, FCVS (Japan), Fellow Endoscopic Spine
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -
Dr. Atmaranjan Dash
MBBS, MS, MCh (Neurosurgery - AIIMS Delhi), Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery, Fellowship in Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Neurosurgery
View More -
Dr. Bhavani Prasad Ganji
MBBS, DNB (Neurosurgery), Ex-Assistant Professor (NIMS)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -
Dr. Bhuvaneswara Raju Basina
MBBS, MS (Orthopaedic Surgery), M.Ch (Neuro Surgery), Fellowship in Spine Surgery (USA), Fellowship in Functional & Restorative Neurosurgery (USA), Fellow in Radiosurgery (USA)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery, Spine Surgery
View More -

Dr. Bikash Kumar Mishra
MD, DM (Neurology), Clinical Fellowship in Pain management (NIH,USA) Epilepsy Fellowship Program (North Carolina, USA)
Neurology
View More -

Dr. Bimal Prasad Padhy
MBBS, MD, DM
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. G Kishore Babu
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Neurology
View More -

Dr. Gaurav Sudhakar Chamle
MBBS, MS General Surgery, DNB Neurosurgery, Fellow in Endoscopic and Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Haritha Koganti
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. J V N K Aravind
MBBS, MS, MCH
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -
Dr. K Sateesh Kumar
MBBS (OSM), MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. K. Vamshi Krishna
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), MCh (Neurosurgery)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Kailas Mirche
MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. Kapil Muley
MBBS, MS, MCH (Neurosurgery)
Neurosurgery, Spine Surgery
View More -

Dr. Laxminadh Sivaraju
MBBS, MCh (Neuro surgery)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. M P V Suman
MBBS, DNB (Gen Med), DrNB (Neurology), PDF (Headache-FWHS)
Neurology
View More -

Dr. Mamindla Ravi Kumar
MBBS, MS, MCh (NIMS), Fellow in Endospine (France) & UBE Spine Surgery (South Korea) & Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery Fellow in Skull Base Surgery (MS Ramaiag and WSBF)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Mandar G Waghralkar
MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine), DM (Neurology), FINR, EDSI
Neurology
View More -

Dr. MGV Aditya
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Neurology
View More -
Dr. Mitalee Kar
MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DNB (Neurology)
Neurology
View More -

Dr. Murali Krishna CH V
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. N.V.S Mohan
MBBS, MCh (Neuro Surgery), DNB
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. P. Chandra Shekar
MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. Parag Rameshrao Aradhey
MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DNB (Neurology)
Neurology
View More -
Dr. Prof. Umesh T
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology), DNB (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. R. Kiran Kumar
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. Ramesh Penkey
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Neurology)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -
Dr. Randhir Kumar
MBBS, MS, MCh
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -
Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
MBBS, MS (Gen. Surgery), MCh (Neurosurgery)
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. S K Jaiswal
MBBS, MD, DM Neurology
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. S N Madhariya
MBBS, MS, MCh
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. S. P. Manik Prabhu
MBBS, M.Ch (Magister of Chirurgiae), Neuro Surgery, MS (General Surgery)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Sandeep Talari
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), MCh (Neurosurgery)
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Sandesh Nanisetty
MBBS, DNB(General Medicine), MNAMS, DM(Neurology), SCE Neurology (RCP, UK), Fellow European Board of Neurology (FEBN)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. Sanjeev Kumar
MBBS, MS, MCh
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Shashank Jaiswal
MBBS, DM (Neurology), PDF (Stroke Intervention), PDF (Epilepsy)
Epilepsy, Neurology
View More -

Dr. Siddharth Sharma
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), MCh (Neurosurgery)
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Sucharita Anand
MBBS, MD Medicine, DM Neurology, PDF Clinical Neuro-Physiology
Neurology
View More -

Dr. Susant Kumar Das
MBBS, MS, MCh (Neurosurgery)
Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Teja Vadlamani
MBBS, DrNB (Neurosurgery)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Venkatesh Yeddula
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), M.Ch (Neurosurgery)
Epilepsy, Neurosurgery
View More -

Dr. Vijay Kumar Terapalli
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), MCh (Neurosurgery)
Neurosurgery
View More -
Dr. Vishal Gaikwad
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM- Neurology
Neurology
View More
Frequently Asked Questions
Couldn’t find what you were looking for?
Need any help? Get a Call Back.

Still Have a Question?

