-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment in Hyderabad
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of your body's deep veins, most often in your legs (DVT). Deep vein thrombosis can cause limb discomfort and edema, but it can also strike without warning.
You may get DVT if you have certain medical conditions that affect how your blood clots. A blood clot in your legs can also occur if you don't move for an extended period of time, such as after surgery or an accident when traveling a long distance, or while on bed rest.
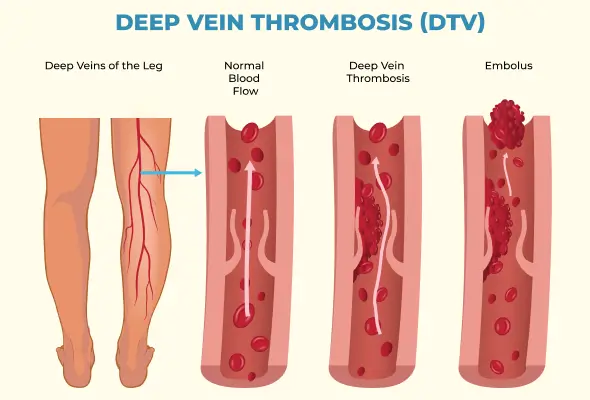
Deep vein thrombosis is a hazardous disorder in which blood clots break loose from your veins, travel through your circulation, and become trapped in your lungs, reducing blood flow (pulmonary embolism). However, pulmonary embolism can occur even when there is no evidence of DVT.
Venous thromboembolism is the combination of DVT and pulmonary embolism (VTE).
Symptoms
The following are some of the indications and symptoms of DVT:
-
The afflicted leg is swollen. Swelling in both legs occurs seldom.
-
Your leg hurts. The pain generally starts in the calf and feels like cramping or soreness.
-
Leg skin that is red or discolored.
-
A warm sensation in the affected limb.
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can arise suddenly.
Diagnosis at CARE Hospitals
In order to diagnose DVT, your doctor will ask you questions regarding your symptoms. You'll also have a physical exam so your doctor can look for areas of edema, discomfort, or skin color changes.
The tests you undergo will be decided by whether your doctor feels you are at low or high risk of DVT. To diagnose or rule out a blood clot, the following tests are used:
-
A D-dimer blood test- A D-dimer blood test is a sort of blood test that examines the quantity of D-dimer, a type of protein, produced by blood clots. D dimer levels in the blood are almost always elevated in persons with severe DVT. A normal D-dimer test result may usually be used to rule out PE.
-
Ultrasound duplex- In this noninvasive examination, sound waves are used to create pictures of how blood flows through your veins. It's the gold standard for detecting DVT. A professional uses a tiny hand-held device (transducer) to gently slide a small hand-held device (transducer) over your skin across the body region being investigated for the test. A series of ultrasounds may be performed over several days to assess if a blood clot is developing or whether a new one has formed.
-
Venography- In a large vein in your foot or ankle, a dye is injected. To search for clots, an X-ray provides a picture of the veins in your legs and feet. The test is rarely used since it is obtrusive. Often, other tests, such as an ultrasound, are conducted first.
-
Scan with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)- This test can be used to identify DVT in the abdominal veins.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment in Hyderabad
DVT therapy has three major objectives.
-
Stop the clot from becoming larger.
-
Prevent the clot from escaping and spreading to the lungs.
-
Reduce your chances of developing another DVT.
Treatment options for DVT include
-
Blood thinners are drugs that thin the blood- The most common therapy for DVT is anticoagulants, often known as blood thinners. However, this Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment in Hyderabad does not eliminate existing blood clots, but they can help keep them from growing larger and reduce your risk of getting more. Blood thinners can be taken orally, delivered intravenously, or injected under the skin. Heparin is usually administered intravenously. Enoxaparin (Lovenox) and fondaparinux are the most regularly used injectable blood thinners for DVT (Arixtra). After a few days of using an injectable blood thinner, your doctor may transfer you to a pill. Blood thinners that may be taken orally include warfarin (Jantoven) and dabigatran (Pradaxa). Some blood thinners don't need to be given by IV or injection initially. Rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis), or edoxaban are the medications in question (Savaysa). They can be begun as soon as the diagnosis is made. It's possible that you'll need to take blood thinners for three months or longer. To avoid major side effects, it's critical to take them exactly as directed. You'll need regular blood tests if you're on warfarin to see how long it takes your blood to clot. Certain blood-thinning drugs should not be taken by pregnant women.
-
Clot busters are substances that dissolve clots- These medicines, also known as thrombolytics, may be administered if you have a more dangerous kind of DVT or PE, or if previous treatments aren't working. These medications are administered by an IV or a tube (catheter) inserted directly into the clot. Clot busters are normally reserved for those who have major blood clots since they might cause serious bleeding.
-
Filters- If you can't take blood thinners, a filter may be put into a major vein in your belly called the vena cava. When clots break free, a vena cava filter prevents them from entering your lungs.
-
Stockings with a high level of compression- These one-of-a-kind knee socks aid in keeping blood from collecting and clotting. Wear them on your legs from your feet to your knees to help minimize swelling caused by deep vein thrombosis. If feasible, wear these stockings during the day for at least two years.
Our Doctors
-

Dr. Tarun Gandhi
MS, FVES
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. P C Gupta
MBBS, MS, FICA, FIVS (Japan)
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Ashish N Badkhal
MBBS, MS, MCh
Vascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Ashok Reddy Somu
MBBS, MD, FVIR
Vascular & Interventional Radiology
View More -

Dr. B. Pradeep
MBBS, MD, DNB, FRCR CCT (UK)
Vascular & Interventional Radiology
View More -

Dr. Mustafa Razi
MBBS, MD
Vascular & Interventional Radiology
View More -

Dr. N. Madhavilatha
MBBS, MS, PDCC
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Radhika Malireddy
MBBS, DNB (General Surgery), DrNB (Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery), Post-Doctoral Fellowship in Diabetic Foot Surgery
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Rahul Agarwal
MBBS, DNB (General Surgery), FMAS, DrNB (Vasc. Surg)
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Rajesh Poosarla
MBBS, MD, DNB, DM (Gold Medalist), EBIR, FIBI, MBA (HA)
Interventional Radiology
View More -

Dr. S. Chainulu
MBBS, DNB (Radio-Diagnosis)
Vascular & Interventional Radiology
View More -

Dr. Santhosh Reddy K
MBBS, MD
Radiology
View More -

Dr. Surya Kiran Indukuri
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), DrNB (Vascular & Endovascular Surgery)
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Suyash Agrawal
MBBS, General Surgery (DNB), Surgical Oncology (DrNB)
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. V. Apoorva
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), DrNB Vascular surgery
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Vamsi Krishna Yerramsetty
MBBS, DNB, FIVS
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More -

Dr. Venugopal Kulkarni
MBBS, MS, MRCS, FRCS
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery
View More
Frequently Asked Questions
Couldn’t find what you were looking for?
Need any help? Get a Call Back.

Still Have a Question?

