-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Dementia
Dementia
Best Treatment of Dementia in Hyderabad, India
Dementia is defined as a condition with a set of symptoms that impact your memory, reasoning, and social abilities. It affects you to the point where they interfere with your regular activities.
The profound impact of dementia extends beyond mere forgetfulness; it encompasses a broad spectrum of cognitive challenges that can profoundly alter a person's ability to engage in normal daily tasks and maintain social connections.
Importantly, dementia is not a singular entity caused by a single factor but is influenced by a myriad of interconnected elements. These contributing factors can vary widely and may include neurological, vascular, or degenerative conditions. Understanding the underlying causes of dementia requires a comprehensive diagnosis, a process facilitated by the expertise available at CARE Hospitals.
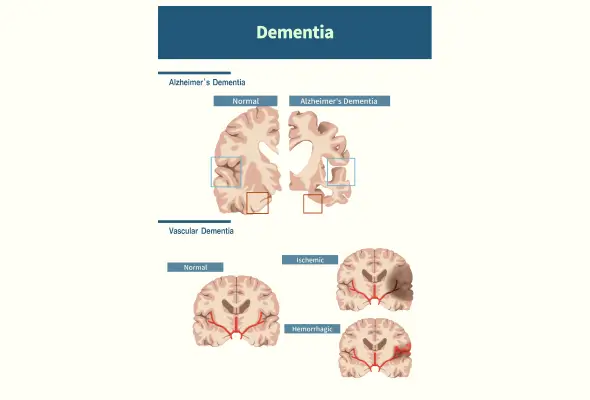
CARE Hospitals offers a thorough diagnostic approach to unravel the complexities of dementia, employing advanced medical assessments and examinations. This allows healthcare professionals to identify the specific factors contributing to an individual's dementia symptoms, paving the way for tailored treatment plans and interventions. By addressing the diverse array of factors contributing to dementia, CARE Hospitals aims to enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by this challenging condition.
What’s the difference between dementia and Alzheimer’s disease?
Dementia is a characterization of an individual's mental functioning and is not a distinct ailment. It serves as an overarching term encapsulating a significant decline in mental faculties that disrupts daily life. Various factors contribute to the development of dementia, with conditions like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease being among the numerous underlying causes. Alzheimer's disease, in particular, stands out as the most prevalent root cause of dementia.
Types of Dementia
Dementia encompasses a diverse range of cognitive disorders grouped into three categories: primary, secondary, and reversible causes. Primary dementia arises as the principal ailment, featuring several distinct types.
Primary Dementia:
- Alzheimer's Disease: The most prevalent form, characterized by the accumulation of abnormal proteins (tau and amyloid) disrupting nerve cell communication. Initial symptoms include short-term memory loss, progressing to confusion and behavioral changes.
- Vascular Dementia: The second most common type, attributed to impaired blood flow, often resulting from strokes or atherosclerosis. Symptoms involve memory issues, confusion, and concentration difficulties.
- Lewy Body Dementia: Involves the formation of protein clumps (Lewy bodies) in brain cells, leading to movement problems, sleep disturbances, memory loss, and hallucinations.
- Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD): Caused by damage to the frontal and temporal brain lobes, resulting in alterations in behavior, personality, language skills, or motor coordination. Common in individuals aged 45 to 64.
- Mixed Dementia: A combination of two or more types, often Alzheimer's with vascular dementia, presenting challenges in diagnosis due to overlapping symptoms.
Secondary Dementia:
- Arises from other diseases such as Huntington's, Parkinson's, Creutzfeldt-Jakob, or Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, each with unique neurological implications.
Causes
Conditions causing dementia-like symptoms that may be treated:
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) involves excess cerebrospinal fluid, treated by draining fluid through a shunt.
- Vitamin deficiencies, infections (HIV, syphilis, Lyme disease, COVID-19), metabolic conditions, medication side effects, and other factors can mimic dementia and may be reversible with appropriate interventions.
- Understanding the distinct categories and types of dementia is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approaches. Comprehensive evaluation is essential to identify the specific causes and provide targeted care.
Symptoms
Dementia is a prevalent disease and has many reasons linked to it. The signs and symptoms can vary from individual to individual. It is divided into cognitive and psychological symptoms.
Cognitive signs and reasons-
-
Memory loss
-
Difficulty communicating or finding words
-
Difficulty with visual and spatial abilities (while driving)
-
Difficulty reasoning or problem-solving
-
Difficulty handling complex tasks
-
Difficulty with planning and organizing
-
Difficulty with coordination and motor functions
-
Confusion and disorientation
Psychological signs and reasons-
-
Personality changes
-
Depression
-
Anxiety
-
Inappropriate behaviour
-
Paranoia
-
Agitation
-
Hallucinations
If you or a loved one is experiencing memory issues or other dementia symptoms, see the best doctors in India at CARE Hospitals to get the best dementia treatment in Hyderabad. The condition can also be caused due to various medicinal effects, hence a proper diagnosis is required prior to the treatment.
Risk Factors
Many factors are related to dementia. The risks can increase as the condition worsens. There are certain conditions and risks that cannot be changed and others can be.
Risks that cannot change-
-
Age- As you become older, your risk for dementia increases. It is especially seen after the age of 65.
-
History of the family- You are more likely to develop dementia if you have a family history of the condition. People who don’t have a genetic history of dementia may encounter the disorder. Genetic mutations can be detected via specific tests.
Risks that can change-
-
Diet and exercise- Lack of exercise has been linked to an increased risk of dementia. One should opt for a healthy diet and follow a routine.
-
Excessive alcohol consumption- Drinking a lot of alcohol has been linked to brain alterations. Alcohol use disorders have been associated with an increased risk of dementia.
-
Cardiovascular disease- High blood pressure (hypertension), high cholesterol, fat buildup in arterial walls (atherosclerosis), and obesity can make a person prone to dementia.
-
Depression- It can be triggered via depression.
-
Diabetes- Diabetes, especially if it is poorly controlled, can raise your risk of dementia.
-
Smoking - This is linked to an increased risk of dementia and blood vessel disease.
-
Pollution of the air- Air pollution particulates hasten the deterioration of the neurological system.
-
Head trauma- People who have had a severe head injury are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) increases the cause of dementia and Alzheimer's disease
-
Sleep disruptions- People with sleep apnea and other sleep problems may be more susceptible to dementia.
Diagnosis
Determining the type of dementia and further conducting diagnosis can be difficult.
-
To diagnose dementia, the doctor must first notice the pattern of loss of skills and functions. It also determines what a person can still do.
-
To detect Alzheimer's disease certain biomarkers are also used.
-
Your doctor will go over your medical history and symptoms and conduct a physical exam.
There are a number of tests conducted to confirm dementia and its cause-
Cognitive and Neuropsychological Tests
Your ability to think will be assessed by doctors at the Dementia Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad. A variety of tests are used to assess cognitive abilities such as memory, orientation, reasoning, and judgment, as well as language and attention skills.
Neurological evaluation
Your memory, language, visual perception, attention, problem-solving, movement, senses, balance, reflexes, and other areas are all evaluated by doctors at CARE Hospitals.
Brain scans
-
CT or MRI scans - These scans can detect signs of a stroke, a haemorrhage, a tumour, or hydrocephalus.
-
PET scans- They are a type of x-ray that is used to reveal patterns of brain activity.
Lab tests
-
Physical disorders that can impact brain function, such as vitamin B-12 insufficiency or an underactive thyroid gland, can be detected with blood tests.
-
Infection, inflammation, and signs of various degenerative disorders are also looked for in the spinal fluid.
Psychiatric
A mental health expert at CARE Hospitals will properly diagnose the symptoms. Diagnosis is conducted to know whether the condition is linked to depression or other mental illnesses.
Prevention of Dementia
While dementia remains challenging to prevent, adopting a health-centric lifestyle can potentially mitigate risk factors associated with certain types of dementia. Prioritizing cardiovascular health by managing cholesterol levels, regulating blood pressure, and controlling blood sugar can contribute to sustaining optimal brain function. Essentially, maintaining an overall state of health ensures that the brain receives the necessary oxygen and nutrients for peak performance. Specific health-promoting actions include:
- Quit Smoking: Cease tobacco use to reduce associated health risks and support overall well-being.
- Embrace a Mediterranean Diet: Adopt a diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, fi sh, shellfish, nuts, beans, and olive oil, while limiting red meat intake.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Incorporate at least 30 minutes of physical activity into most days of the week to promote cardiovascular health.
- Mental Stimulation: Keep the brain active through activities like solving puzzles, playing word games, and engaging in mentally stimulating pursuits, potentially delaying the onset of dementia.
- Social Interaction: Stay socially active by interacting with others, discussing current events, and engaging the mind, heart, and soul in meaningful ways.
Treatment for Dementia
-
Occupational therapy- An occupational therapist can teach you coping skills and show you how to make your home safer. The goal is to prevent mishaps like falls, control behaviour, and prepare you for the onset of dementia.
-
Changing the surroundings- It is comparatively easy for someone with dementia to focus and function when the clutter and loudness are reduced.
-
Tasks are being simplified- Break down difficult activities into smaller segments and concentrate on accomplishments. Structure and routine will make a person less confused.
-
Medication - The doctors will prescribe the right medication according to the patient’s requirements and needs.
Our aim at CARE Hospitals is to serve the patients with the best healthcare services in India. Dementia has been reported as a common disorder in the world. With the help of experts, clinicians and medical professionals at CARE Hospitals, we may provide you with the right treatment with the proper diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Couldn’t find what you were looking for?
Need any help? Get a Call Back.

Still Have a Question?

