-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Carotid Artery Blockage
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Carotid Artery Blockage
Carotid artery stenosis happens when large blood vessels on both sides of your neck narrow because of plaque buildup. These crucial arteries carry oxygen-rich blood to your brain, face, and head. A blockage restricts normal blood flow and makes you more likely to have a stroke. Carotid artery stenosis contributes to about 25% of all ischemic strokes worldwide.
People face a higher risk of this condition as they age. Statistics show that about 10% of people develop carotid artery blockage by their 60s. The risk rises even more for smokers and those with high blood pressure and dyslipidemia.
This article explains the mechanisms, symptoms and treatment options for carotid artery stenosis. Early detection and proper management of this condition are vital steps that can reduce stroke risk by a lot and save lives.
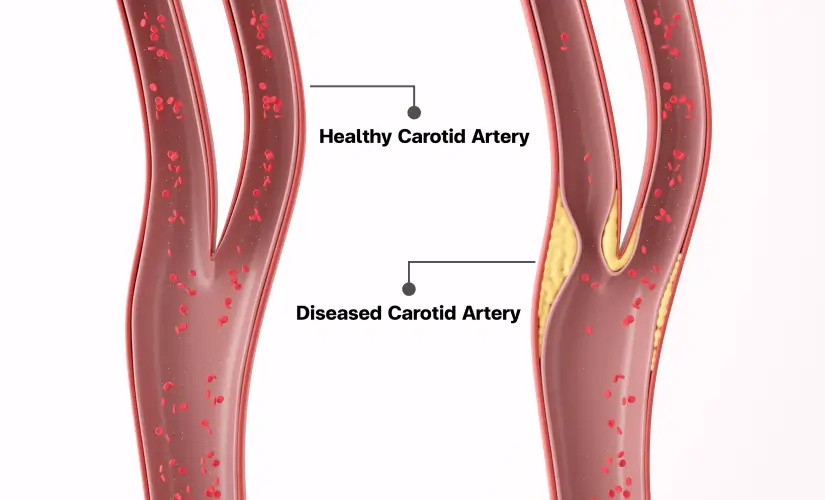
What is Carotid Artery Blockage?
Carotid arteries supply blood to the brain. With time these arteries can become narrow due to atherosclerosis (fat & cholesterol deposits) which eventually reduces the blood flow thus making you more susceptible to the development of blood clots. If a clot blocks blood flow to the brain, it can cause a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). Research shows this is more common in men than women.
Symptoms of a Carotid Artery Blockage
Most people don't feel any symptoms until the blockage gets serious. But watch out for these warning signs:
- Sudden numbness or weakness, mainly on one side of your body
- Problems seeing or temporary blindness in one eye
- Trouble speaking or understanding others
- Unexplained dizziness, confusion, or poor balance
Your doctor might hear a "bruit" - a whooshing sound through their stethoscope that shows disturbed blood flow.
Causes of Carotid Artery Blockage
Atherosclerosis is the main cause. Plaque slowly builds up on your artery walls' inner lining. This starts with damage to the arterial wall, usually from high blood pressure, smoking, or high cholesterol levels.
Risk of Carotid Artery Blockage
Your chances of getting this condition go up with:
- Getting older
- High blood pressure - makes it three times more likely
- Smoking - makes it almost seven times more likely
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Not enough exercise
- Prior radiation therapy to the neck
- Injury to the coronary artery
Complications of Carotid Artery Blockage
Stroke is the most dangerous outcome - it happens when part of your brain loses its blood supply.
Carotid artery blockage can also cause:
- Permanent brain damage
- Vision issues like partial or complete vision loss
- Temporary or permanent paralysis or weakness on one side of the body
- Difficulty in concentrating
- Loss of balance and coordination
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Blockage
Doctors will ask about your symptoms and check your balance. Your doctor might detect an unusual sound called a "bruit" through a stethoscope while examining your neck.
Diagnostic tests:
- Carotid ultrasound or Doppler: Sound waves create images of your arteries and measure blood flow painlessly.
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA): X-rays combined with contrast dye provide detailed views. This works well for patients with pacemakers.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): The process creates detailed images without using radiation.
- DSA / Cerebral angiography: A catheter guides contrast material directly into the arteries while X-ray imaging captures detailed pictures. This procedure is minimally invasive.
Treatment for Carotid Artery Blockage
- Lifestyle changes help manage mild to moderate blockages:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Stopping smoking habits
- Controlling blood pressure
- Medicines: Blood pressure reducers, cholesterol-lowering statins, or daily aspirin might help prevent blood clots.
- Severe blockages need surgical treatment through:
- Carotid endarterectomy: The surgeon removes plaque through an incision in your neck.
- Carotid stenting: This less invasive procedure uses a balloon to open the artery. A stent keeps it expanded afterwards.
When to See a Doctor
You need immediate medical attention if you experience sudden weakness, vision changes, speaking difficulties, or a severe headache. These symptoms could indicate a mini-stroke or stroke that requires urgent care.
Conclusion
Carotid artery blockage is a serious health concern that you can manage with proper awareness and medical help. This condition affects only a small number of people, but it can change lives forever.
Your chances of recovery improve by a lot if doctors detect it early. Get immediate medical help if you notice warning signs like sudden weakness on one side, vision changes, speech problems, or unexpected dizziness.
Healthy lifestyle choices can make a huge difference. Regular check-ups are a great way to get ahead of problems, especially when you have risk factors. Your carotid artery health depends on prevention and early treatment - these truly save lives.
FAQs
1. What are the first signs of a blocked carotid artery?
Many patients don't notice any symptoms or weakness until they have a mini-stroke or TIA. The warning signs include sudden dizziness, fainting, blurred vision, or numbness in limbs. Blood flow disruptions to the brain can occur before a full stroke develops.
2. How serious is carotid artery stenosis?
This is a critical condition that significantly increases your stroke risk. Even small blockages can raise stroke chances over time. Carotid artery disease leads to one-third of all strokes. Stroke remains the third leading cause of death in developed nations.
3. Can you unblock a carotid artery without surgery?
Mild to Moderate blockages respond well to non-surgical treatments such as:
- Aspirin and other antiplatelet medications
- Statins that help stabilise plaques
- Blood pressure management
- Changes in lifestyle habits
Doctors recommend surgery when blockages reach 70% or higher.
4. What are the warning signs of a blocked carotid artery?
Key signs include:
- One side of the face droops
- Speech becomes slurred or communication gets difficult
- Vision dims or darkness covers one eye
- One side of the body feels weak
5. What foods should you avoid with carotid artery blockage(stenosis)?
Stay away from foods rich in:
- Saturated fats from red meat and dairy
- Trans fats in processed foods
- Sodium that raises blood pressure
- Sugar
Still Have a Question?


