-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Best Hospital for Brain Haemorrhages Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Advanced Technology
- Shorter Hospital Stay
- Pre & Post-Operative Care
- All Insurance Accepted

Chat With Our Experts
Get second opinion on Whatsapp
25 lakhs+
Happy Patients
Experienced and
skilled surgeons
17
Health Care Facilities
Top most Referral Centre
for Complex Surgeries
Advanced Brain Haemorrhage Surgery in Bhubaneswar
Blood vessels in the brain sometimes leak or burst, causing a haemorrhage in the brain. This dangerous condition leads to bleeding inside brain tissue or between the brain and skull. Research shows brain haemorrhages make up about 13% of all strokes. Collected blood or intracranial hematoma puts pressure on brain tissue, leading to headaches, confusion, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. This fatal condition requires immediate medical intervention to prevent severe brain damage or complications.
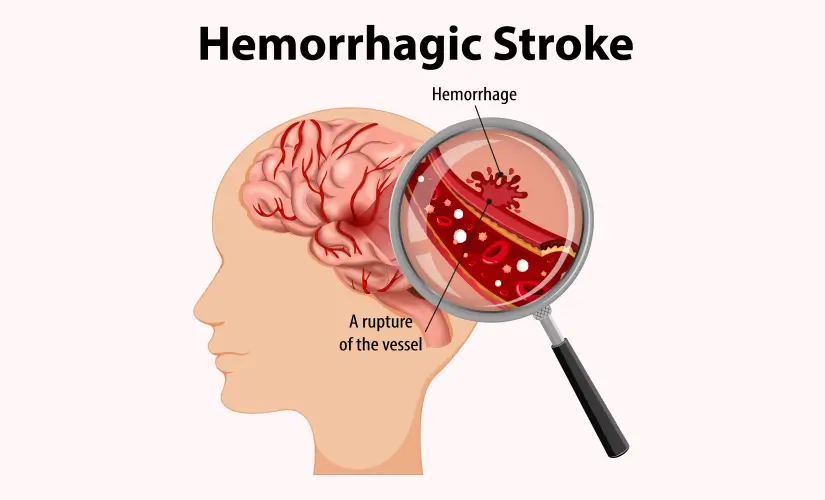
What are the Types of Haemorrhages in the Brain?
Brain haemorrhages happen in two main areas: the space between the skull and brain tissue and deep inside the brain tissue. The first category has three distinct types:
- Epidural Haemorrhage: Occurs between the skull and the dura mater (outer protective layer). This type usually results from skull fractures and can affect either arterial or venous bleeding.
- Subdural Haemorrhage: Develops between the dura mater and the middle membrane layer. Blood vessels that connect the brain and skull can stretch or tear, leading to this condition.
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: Forms between the middle and innermost protective layers. Trauma or aneurysm rupture can cause this type.
The brain tissue itself can experience two other types:
- Intracerebral Haemorrhage: Affects the lobes, brainstem, and cerebellum regions. Strokes most commonly cause this type.
- Intraventricular Haemorrhage: Develops in the brain's ventricles where cerebrospinal fluid production takes place.
Best Brain Haemorrhages Surgery Doctors in India


What Causes Brain Haemorrhages?
Blood pressure that remains high creates a major risk, especially when you have no treatment. Blood vessel walls become weak under constant pressure and might rupture. Blood vessel problems are vital factors, too, including:
- Aneurysms - balloon-like bulges in arteries that can burst
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVM) - present from birth
- Amyloid angiopathy - we noticed this mostly in older adults
- Blood disorders - including haemophilia and sickle cell anaemia
- Liver conditions - increasing overall bleeding risks
- Brain tumours - raising susceptibility to haemorrhages
Signs of Brain Haemorrhages
Quick recognition of brain haemorrhage symptoms plays a significant role in treatment outcomes. These signs typically appear suddenly and can worsen over time.
The most common warning signs include:
- A sudden, severe headache, often described as a 'thunderclap' headache
- Weakness or numbness that affects one side of the body
- Slurred speech and confusion
- Vision changes or sensitivity to light
- Balance and coordination problems
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures in people without previous history
- Stiff neck and difficulty swallowing
Diagnostic Tests for Brain Haemorrhages
- CT Scans: Brain CT scans are the most reliable diagnostic tool that shows acute blood appearing much brighter than brain tissue. Medical teams often use contrast dye during CT scans to get a better view of blood vessels. This approach, called CT angiography (CTA), reveals the exact location and size of the bleeding area.
- MRI Scans: MRI technology provides enhanced diagnostic insights. Research shows that MRI performs better than CT scans to detect small haemorrhages and pinpoint their exact position. Both methods are valuable, but MRI excels at finding abnormalities beneath the surface, especially with suspected tumours.
- Angiography: Doctors turn to cerebral angiography for complex situations. The procedure involves threading a catheter through blood vessels to the brain while a special dye reveals issues under X-ray imaging. This method becomes crucial when standard scans don't provide clear results.
The diagnostic toolkit also includes:
- Electroencephalogram to assess brain activity
- Complete blood count to review bleeding disorders
- Lumbar puncture to find blood in spinal fluid
Treatments for Brain Haemorrhages
- Emergency Management: The main priorities are controlling blood pressure and managing pressure inside the skull. Doctors may use oxygen therapy, IV fluids, and emergency medications.
- Medications: Doctors prescribe blood pressure medications when a patient's systolic blood pressure ranges between 150 and 220 mmHg. Doctors also give their patients:
- Antiseizure medications to prevent convulsions
- Corticosteroids to reduce brain swelling
- Pain relievers to manage headaches
- Stool softeners to prevent strain
- Antianxiety medications to keep patients calm
- Surgery: Severe cases require surgery. Surgical options include:
- Craniotomy: Open brain surgery to stop the bleeding, remove the clot, and relieve pressure.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Utilises a catheter or endoscope for clot removal in select cases
- Craniectomy: Involves drilling through the skull to relieve pressure
- Drainage Procedures: Sometimes, doctors insert a catheter that drains excess fluid.
Why Choose CARE Hospitals for a Brain Haemorrhages Procedure?
CARE Hospitals in Bhubaneswar excels at treating brain haemorrhage cases. Research confirms that specialised stroke units help patients survive better and increase their chances of returning home.
Quick response and expert care define the hospital's core strength. The hospital's strengths include:
- Dedicated stroke unit with round-the-clock emergency care
- Multidisciplinary team of neurointensivists
- Advanced diagnostic and surgical facilities
- Detailed rehabilitation services
- Personalised post-operative care protocols
Brain Haemorrhages Surgery Hospitals in India
-

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad

CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad

CARE Hospitals, HITEC City, Hyderabad

CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City, Hyderabad

Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad, Hyderabad

CARE Hospitals, Nampally, Hyderabad

CARE Hospitals, Malakpet, Hyderabad

CARE Hospitals, Bhubaneswar

Ramkrishna CARE Hospitals, Raipur

CARE Hospitals, Ramnagar, Visakhapatnam

CARE Hospitals, Health City, Arilova
Related Surgeries
- Best Hospitals for Laminectomy Surgery in Hyderabad
- Best Hospital for VP Shunt Surgery in Hyderabad
- Best Hospital for Polytrauma Surgery in Hyderabad
- Best Hospitals for Cervical Spondylosis Surgery in Hyderabad
- Best Hospital for Brain Haemorrhages Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospital for Lumbar Canal Stenosis Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospital for Brain Tumor Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospitals for Lumbar Disk Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospital for Stroke Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospital for Spinal Fracture Treatment in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospital for Traumatic Head Injury Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospital for Trigeminal Neuralgia Surgery in Bhubaneswar
- Best Hospital for Microvascular Decompression Surgery in Hyderabad
- Best Hospital for Complex Brain Tumour Surgery in Hyderabad
Frequently Asked Questions
CARE Hospitals are the top choices for brain haemorrhage treatment in Bhubaneswar. These facilities have detailed neurosurgical care with experienced specialists and advanced diagnostic equipment.
The best treatment depends on the haemorrhage type and how severe it is. Blood pressure control and medications work well as medical management options. In spite of that, severe cases need surgical intervention, and minimally invasive techniques show promising results.
Yes, recovering is possible, though each patient's experience is different. The outcome depends on the haemorrhage's size, location, and how quickly treatment begins.
Both tests help diagnose the condition, and MRI shows small haemorrhages and exact locations better. CT scans remain the first choice in emergencies because they are faster and more readily available.
Of course, non-surgical treatment works for patients with mild symptoms or specific haemorrhage locations. Treatment options include:
- Blood pressure management
- Clotting factor administration
- Intracranial pressure monitoring
- Medications for brain swelling
Recovery results vary substantially. Many survivors adapt to a "new normal" and adjust their daily routines. They might need ongoing management for fatigue, memory problems, and occasional headaches.
Patients should stay away from activities that raise intracranial pressure. They shouldn't lift anything over 10 pounds, bend at the waist, or operate heavy machinery.
Recovery needs careful attention to diet and activities. Doctors advise limiting salt, as well as avoiding too much sugar and alcohol. A doctor should supervise as physical activities are slowly reintroduced.
Still Have a Question?


















