-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Uric Acid Symptoms
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Uric Acid Symptoms
Uric acid is a waste product of the body that is found in the blood. It is a normal waste component of our body, but it can become concentrated or increase in the blood (Hyperuricemia), causing health problems such as gout, kidney stones, joint and tissue damage, etc.
What is Uric Acid?
Uric acid is a waste product found in the blood. It is produced when the body processes and breaks down chemicals known as purines. Uric acid dissolves in the blood, passes through the kidneys, gets mixed with urine, and is expelled from the body. If uric acid remains in the body, its concentration can lead to a condition called hyperuricemia, which has the potential to cause damage to various body parts and organs.
Uric Acid levels in males and females
Uric acid is a normal component of blood, so there is always some amount of uric acid present. Persistently higher than-normal levels of uric acid can be a cause for concern in both men and women. High uric acid symptoms in females or males can also become lower than a certain amount, which may indicate a condition where uric acid is being expelled from the body in larger amounts than normal.
Uric acid levels are measured in milligrams (mg) per deciliter (dL). The healthy and abnormal uric acid levels differ for men and women, as provided below.
|
Uric Acid Levels |
Men |
Women |
|
Normal |
2.5-7 mg/dL |
1.5-6 mg/dL |
|
Higher |
> 7 mg/dL |
> 6 mg/dL |
|
Lower |
< 2 mg/dL |
< 1.5 mg/dL |
Causes of Uric Acid
The accumulation of uric acid in the body can occur, although the exact reasons are not clear. There are certain risk factors that contribute to uric acid accumulation, such as diet and environmental factors. These risk factors may include:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Diuretics
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Certain immunosuppressive medications
Dietary factors, such as foods and drinks that contain purines or can elevate purine levels, including red meats, some seafood, and alcohol, as well as a diet high in fructose, primarily found in processed foods and drinks, can lead to a higher concentration of uric acid in the body.
Uric acid has also been associated with certain medical conditions and treatments:
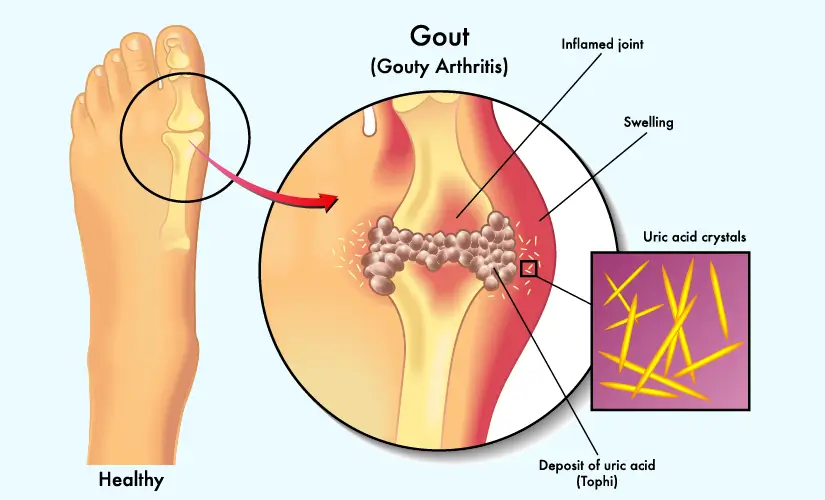
- Gout: Individuals suffering from gout, a condition that affects the joints, experience the accumulation of uric acid in these joints, resulting in symptoms such as swelling, pain, and discolouration.
- Kidney diseases: The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood. In cases of kidney diseases, the filtration process is hindered, leading to the improper elimination of waste products, including uric acid. As a result, the level of uric acid in the blood rises.
- Cancer treatment: Chemotherapy, a treatment used for cancer, may kill both cancerous and healthy cells, releasing purines in the process. This can lead to uric acid increase symptoms.
Symptoms of high levels of Uric Acid
A person with a higher or lower concentration of uric acid than normal may or may not exhibit any symptoms. Sometimes symptoms may manifest after a significant period of time has passed and the normal levels of uric acid have been consistently exceeded. This can lead to health problems. Additionally, individuals may experience accompanying uric acid symptoms related to other health conditions such as gout and kidney diseases.
Symptoms associated with high uric acid levels causing gout may include:
- Painful or swollen joints
- Discolouration or shiny skin around the joints
- Joints feeling warm to the touch
Symptoms of kidney stones that may have been caused by uric acid may include:
- Pain in either side of the back
- Frequent urination
- Urine looks cloudy or contains blood or smells unusual
- Nausea or vomiting
Cases of low uric acid are less common than high uric acid. Low uric acid symptoms may include frequent urination, which can lead to dehydration.
When should I see the doctor?
As mentioned above, uric acid can cause painful symptoms such as gout or kidney stones. If you experience symptoms like back pain or joint inflammation, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Risk Factors of Uric Acid
Risk factors for elevated blood uric acid levels include:
- Excess Weight: People who are significantly overweight or obese have an increased likelihood of experiencing high uric acid levels.
- Dietary Habits: Regular consumption of purine-rich foods can contribute to elevated uric acid levels. These foods encompass red meat, organ meat, and certain seafood like scallops, mollusks, and tuna. Additionally, the consumption of foods and beverages sweetened with fructose syrup can also lead to heightened uric acid levels.
- Kidney Issues or Injury: Kidney damage can impair the kidney's ability to efficiently filter waste products, resulting in the accumulation of uric acid in the bloodstream.
How is high Uric Acid diagnosed?
When visiting the doctor, they may request your medical history and conduct specific tests. Symptoms of gout and kidney stones will be thoroughly evaluated. The doctor may also recommend a uric acid test to measure the amount of uric acid in the blood or urine. A joint aspiration may be performed, involving the removal of a small amount of fluid from a swollen joint to check for the presence of uric acid, indicating gout.
Cancer patients undergoing treatment may undergo regular monitoring as a first step to treat high uric acid. Symptoms related to uric acid may not often manifest. Individuals with uric acid issues may need to be tested every six months.
Prevention
The most effective way to prevent hyperuricemia is by adopting a healthy diet and exercise routine. Reducing the frequency of consuming foods and beverages high in purines can help lower your uric acid levels and promote overall health.
Consult your healthcare provider to find out which foods or drinks you should limit and how often you can safely include certain high-purine options in your diet.
Purine-Rich Foods
Many of these foods are known to elevate uric acid levels, trigger inflammation, impact heart health, and potentially lead to diabetes. These include:
- Red meat, particularly organ meats such as liver and kidney
- Alcohol, especially beer
- Sugary beverages, candy, and desserts
- Saturated fats found in red meat, butter, cream, ice cream, and coconut oil
- Both sweetened and unsweetened fruit juices, with the exception of cherry juice
- Certain seafood, like shellfish, anchovies, and tuna, were once considered unsuitable for individuals with gout. However, it is now believed that the health benefits of moderate fish consumption outweigh the potential risks.
Living with Hyperuricemia
Following a healthy diet and exercise routine can help you achieve a healthy weight and lower your uric acid levels. If you have hyperuricemia, making dietary adjustments, increasing your water intake, and staying active can decrease the likelihood of experiencing gout flares and other related symptoms in the future.
Treatment of high levels of Uric Acid
In the case of initial high uric acid symptoms, treatment may involve following a low-purine diet. It helps to decrease the purine concentration, thus decreasing uric acid levels. The doctor may advise restricting the intake of certain foods and beverages, such as alcohol, red meat, and shellfish.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended for reducing inflammation caused by gout. In some cases, specific medications can also help reduce inflammation.
Kidney stones may pass naturally or sometimes require medical intervention. The doctor may suggest increasing water intake and avoiding soft drinks and alcohol.
When to see a doctor
See your healthcare provider if you experience any new symptoms, such as:
- Swelling
- Discoloration or redness
- Warmth or heat in a joint
- Difficulty urinating
- Pain during urination
- Pain after urinating
Conclusion
Abnormal uric acid levels are a common condition, but symptoms may not always be present. The treatment for this type of condition depends on whether it is causing high or low levels. For comprehensive treatment of abnormal uric acid levels and its associated conditions, visit CARE Hospitals.
FAQs
1. What happens if uric acid levels are high?
High uric acid levels can lead to the accumulation of uric acid in various parts of the body, resulting in conditions like gout and kidney stones. These conditions can be appropriately treated with proper diagnosis.
2. What are the main causes of high uric acid?
The exact causes of high uric acid levels are unknown, but there are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing problems associated with higher or lower uric acid levels than normal.
3. Which foods help remove uric acid?
Eat fiber-rich food such as lentils, nuts, oats, quinoa, brown rice, etc. vitamin C foods such as oranges, grapefruit, kiwi, etc., and avoid alcohol. This might help you to regulate uric acid levels in the body.
4. Which foods should be avoided for uric acid?
To reduce uric acid concentration in the blood, it is advisable to avoid alcohol, processed foods and drinks, and reduce consumption of red meats.
5. At what age can uric acid start to increase?
Uric acid levels can become higher or lower than normal at any age and can affect anyone.
6. How long can uric acid-related conditions last?
Gout, caused by high uric acid, may resolve on its own within a few weeks. Kidney stones may also pass on their own, however, treatment may be required in some conditions.
7. How can I reduce my uric acid?
Drink plenty of water, avoid high-purine foods (like red meat and seafood), limit alcohol, and maintain a healthy weight. Sometimes, medication might be needed.
8. How to check uric acid at home?
You can use a home testing kit that involves pricking your finger to get a small blood sample. Follow the instructions on the kit to get your uric acid level.
9. What exercise is good for uric acid?
Regular, moderate exercise like walking, cycling, and swimming can help reduce uric acid levels. Avoid intense workouts that can increase uric acid.
10. Can lemon remove uric acid?
Lemon juice can help reduce uric acid levels because it makes your body more alkaline, which helps dissolve uric acid.
11. Will uric acid cause pain in joints?
Yes, high uric acid levels can cause gout, which leads to painful joint inflammation, especially in the big toe.
12. Which doctor treats uric acid problems?
A rheumatologist specializes in treating gout and other joint-related issues, but your primary care doctor can also help manage uric acid levels.
13. Can uric acid increase without any symptoms?
Yes, high uric acid levels can be asymptomatic, meaning you might not have any noticeable symptoms until it causes a problem like gout.
14. Which medications are used to treat high uric acid?
Common medications include allopurinol, febuxostat, and probenecid, which help reduce uric acid production or increase its excretion.
15. What foods cause uric acid?
Foods high in purines, like red meat, organ meats, seafood, sugary drinks, and alcohol (especially beer), can increase uric acid levels.
16. What happens if uric acid is high?
High uric acid can lead to gout, kidney stones, and kidney damage if left untreated. It's important to manage and monitor uric acid levels to prevent complications.

Still Have a Question?



