-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Obesity: Causes, Health Risks and Treatment Options
Updated on 31 March 2022

Table of Content
Obesity is defined as having excess body fat. Adults 18 years of age and older with a BMI greater than 32.5 are considered morbidly obese. In this blog, we'll learn more about obesity causes, symptoms, and treatment. Also, we'll go through daily habits on how to prevent being overweight.
It is a chronic medical disease that can lead to diseases like
- Diabetes
- high blood pressure
- obesity-associated cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease, gallstones
- Obesity is a risk factor for a number of
Obesity has an extremely high relapse rate. Most people who lose weight regain the weight within five years.
Even though medications and diets can help, The treatment of obesity is a lifelong commitment which includes healthy dietary habits, increased and regular physical activity. One cannot completely rely on medications and diet and resort to short-term “fix”
The goal of treatment should focus on achieving and maintaining a “healthier weight” rather than the ideal weight. significant health benefits such as lowered blood pressure, risks of diabetes and heart disease reduced are noticeable even with a modest weight loss of 5%-10% of the initial weight.
Obesity and Overweight
Overweight and obesity usually refer to weight greater than what is healthy by the height of an individual.
While body fat is necessary for storing energy, heat insulation, shock absorption, and other functions. But an excess of the same, results into the chronic condition of obesity
Body mass index (BMI)
- It is the most reliable parameter for defining
- It is determined by a person’s height and weight. BMI equals a person’s weight in kilograms (kg) divided by their height in metres (m) squared.
- Since BMI describes body weight relative to height, there is a strong correlation with total body fat content in adults:
- Normal: BMI of 5-24.9
- Overweight: BMI of 25-29.9
- Obese: BMI over 30
- Morbidly obese individual: BMI>32.5
Causes of Obesity
Obesity results from a complex interplay of factors, including diet, genetics, inactivity, and environmental influences. Here are the causes of obesity.
- Genetics - A person is more likely to be obese if one or both parents are
- Genetics also have a role to play in hormones involved in fat
- Leptin deficiency - Leptin is a hormone produced in fat cells and in Leptin asserts control by signalling the brain to eat less when body fat stores are too high. If, for some reason, the body cannot produce enough leptin or leptin cannot signal the brain to eat less, this control is lost, and obesity occurs.
- Researchers are still exploring Leptin replacement as a treatment for
- Morbid obesity may happen when leptin insensitivity occurs.
- Physical inactivity - Sedentary people burn fewer calories than people who are active therefore showing strong correlations between physical inactivity and weight gain in both sexes
- Diet high in simple carbohydrates - With the intake of carbohydrates, there is an increase in blood glucose level which in turn stimulates insulin release by the pancreas, and insulin promotes the growth of fat tissue and can cause weight
- Although The role of carbohydrates in weight gain is not clear, it is believed that simple carbohydrates such as beer, wine etc have a greater contribution than complex carbohydrates as the former has a more pronounced insulin
- Overeating leads to weight gain, especially if the diet is high in fat as it has a much higher energy
- Frequency of eating - This is a rather debated
- There are reports that state that people who eat small meals with a high frequency tend to have lower cholesterol levels and stable blood sugar levels than compared to people who have larger meals with a much lower
- An explanation for the same could be that small frequent meals produce stable insulin levels, whereas large meals cause large spikes of insulin after
- Medications associated with weight gain include
- antidepressants
- anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine and valproate
- some diabetes medications
- hormones such as oral contraceptives
- corticosteroids such as
- high blood pressure medications
- Psychological factors - emotions have a strong influence on eating habits. Many people binge eat in response to emotions such as boredom, sadness, stress, or
- Diseases: Diseases such as hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, Prader-Willi syndrome, PCOS, and Cushing’s syndrome are also major contributors to
- Social issues: There is a definite link between social issues and
- Lack of money to purchase healthy foods or lack of safe places to walk or exercise can increase the risk
Health risks
Obesity is not merely a cosmetic consideration; it also increases the risk of developing a number of chronic diseases, including the following:
- Insulin Insulin is necessary for the transport of blood glucose into the cells of muscle and fat.
- By transporting glucose into cells, insulin keeps the blood glucose levels in the normal
- Insulin resistance (IR) is the condition whereby there is diminished effectiveness of insulin in transporting glucose into Fat cells are more insulin resistant than muscle cells.
- The pancreas initially responds to insulin resistance by producing more As long as the pancreas can produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance, blood glucose levels remain normal. Once the pancreas can no longer keep up with producing high levels of insulin, blood glucose levels begin to rise, resulting in type 2 diabetes, thus insulin resistance is a pre-diabetes condition.
- Type 2 (adult-onset) diabetes- The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with the degree and duration of
- It is associated with central obesity; a person with central obesity has excess fat around his/her waist
- Hypertension is common among obese adults. A study showed that weight gain tended to increase blood pressure in women more significantly than in
- High cholesterol
- Stroke
- Heart A study found that the risk of developing coronary artery disease increased three to four times in women who had a BMI greater than 29.
- In patients who have already had a heart attack, obesity is associated with an increased likelihood of a second heart
- Cancer- Obesity is a risk factor for cancer of the colon in men and women, cancer of the rectum and prostate in men, and cancer of the gallbladder and uterus in
- Obesity may also be associated with breast cancer, particularly in postmenopausal women. Fat tissue is important in the production of oestrogen, and prolonged exposure to high levels of oestrogen increases the risk of breast
- Gallstones
- Gout and gouty arthritis
- Osteoarthritis Of the knees, hips, and the lower back
- Sleep apnea
Factors
- Ethnicity- Ethnicity may influence the age of onset and the rapidity of weight
- Childhood weight- A substantial link has been found between a person’s weight during childhood, teenage years, and early adulthood and the development of adult
- Therefore, decreasing the prevalence of childhood obesity is one of the areas to focus on in the fight against
- Hormones- Women tend to gain weight, especially during certain events such as pregnancy, menopause, and in some cases, with the use of oral
How is obesity treated
The treatment for obesity typically involves dietary modifications, increased physical activity, behavior changes, and, in some cases, medical or surgical interventions.
- Healthy eating plan and regular physical activity- Following a healthy eating plan with fewer calories is often the first step in trying to treat overweight and
- It should be coupled with regular physical activity. Being active helps in using Regular physical activity also helps in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Habitual Changes- Changing your eating and physical activity habits and lifestyle is difficult, but with a plan, effort, regular support, and patience, you may be able to lose weight and improve your
- The following tips may help you think about ways to lose weight, engage in regular physical activity, and improve your health over the long term.
- Setbacks are normal- After a setback, like overeating. regrouping and focusing on getting back to the healthy eating plan is
- Set goals- Having specific goals helps one stay on track. Rather than be abstract, set a more tangible goal
- Seek support.-Help or encouragement from family, friends, or health care professionals goes a long It can either be through a virtual medium, such as a phone call, or in person.
- Weight-management programs- In a weight-management program, trained weight-management specialists design a broad plan and help in carrying out as per individual
- Plans include a lower-calorie diet, increased physical activity, and ways to help make habitual
- Weight-loss medicines- When healthy eating and physical activity habits do not suffice, then doctors may prescribe medicines to treat overweight and
- Though it is still important to accompany the medication with healthy eating and regular physical activity
- Weight-loss devices- There is no long-term data on the safety and effectiveness of weight loss devices as they have only recently been approved. Weight-loss devices include
- The following tips may help you think about ways to lose weight, engage in regular physical activity, and improve your health over the long term.
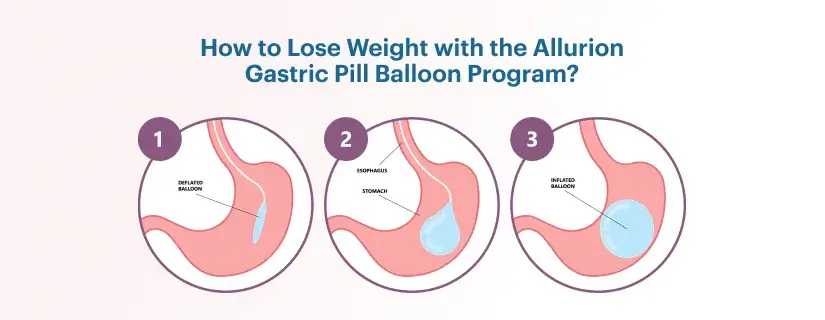
- Gastric balloon system- For the gastric balloon system, a doctor places one or two balloons in the stomach through a tube that goes in the mouth. Once the balloons are in the stomach, the surgeon fills them with salt water so they take up more space in your stomach and help you feel
- Bariatric surgery- Bariatric surgery is an option to deal with extreme obesity and at lower levels of obesity if one has serious health problems, such as type 2 diabetes or sleep
- Special diets
- Calorie-restricted diets- doctors may recommend a lower-calorie diet such as 1,200 to 1,500 calories a day for women and 1,500 to 1,800 calories a day for men. The calorie level depends on the body weight and physical activity
- A lower-calorie diet with a variety of healthy foods will give you the nutrients you need to stay
- Calorie-restricted diets- doctors may recommend a lower-calorie diet such as 1,200 to 1,500 calories a day for women and 1,500 to 1,800 calories a day for men. The calorie level depends on the body weight and physical activity
- Intermittent fasting- There is no long-term data on the safety and effectiveness of intermittent fasting for long-term weight But it has recently gained attention as a strategy for weight loss and health benefits
Conclusion
Maintaining the ideal body weight is a balancing act between food consumption and calories needed by the body for energy. You are what you eat.
It has been established that eating proper foods can influence health for all age groups. According to research, A Diet should mainly comprise of
- plenty of grain products, vegetables, and fruits.
- low in fat, and saturated fat,
- moderate in salt
- If you drink alcoholic beverages, do so in
CARE Hospitals is one of the best weight loss hospitals in Hyderabad offering the latest technologies for bariatric treatment.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (38)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
10 Myths of Bariatric Surgery You Must Know
Changing Trends in Bariatric Surgery
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Bloating During Ovulation: Symptoms, Causes and Remedies
3 March 2026
Read More
-

Itching During Dengue: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
3 March 2026
Read More
-

Cervical Cerclage: Types, Procedures, Precautions and Risks
3 March 2026
Read More
-

What is a Good AMH Level to Get Pregnant
3 March 2026
Read More
-

Zinc Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
2 March 2026
Read More
-

Chest Pain When Coughing: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
2 March 2026
Read More
-

12 Health Benefits of Eating Mushrooms
2 March 2026
Read More
-

7 Health Benefits of Blood Donation You Should Know About
2 March 2026
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.