-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD): What it is, Procedure, Side Effects and Recovery Process
Updated on 23 January 2024

Table of Content
- Who May Need Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection?
- Before Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- During Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Recovery After Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Advantages of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Side Effects of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Difference Between Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) and Dissection (ESD)
Advancements in medical technology have revolutionised the treatment landscape for gastrointestinal conditions. One such breakthrough procedure, Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD), has garnered attention for its minimally invasive approach and efficacy in treating early-stage gastrointestinal tumours. The doctor could advise endoscopic submucosal dissection to remove a tumour or lesion if it is located inside the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
ESD is an advanced technique used to remove abnormal tissues or early-stage tumours from the digestive tract. It is a minimally invasive treatment that removes precancerous and cancerous regions from the Gastrointestinal (GI) tract using an endoscope, a flexible, tube-like device. It may be challenging to fully remove these tumours using conventional techniques since they may be near muscular tissue. Your doctor can access your GI system with endoscopic procedures without making any incisions. Depending on the area of the digestive tract they're treating, doctors may enter the endoscope into your mouth or anus (butthole). After that, they use the endoscope to implant surgical instruments to remove abnormal tissue. Compared to open surgery, this method allows the patient to recuperate more quickly and with less discomfort.
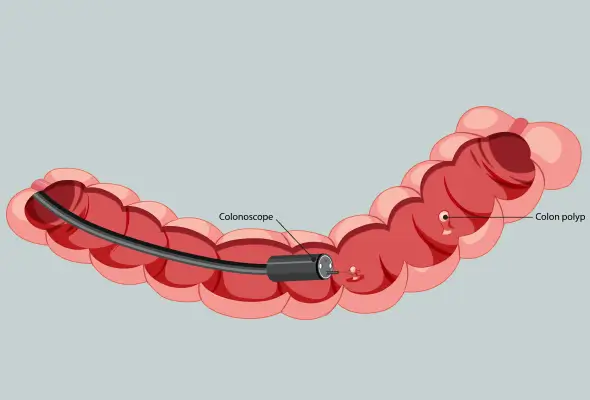
Who May Need Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection?
Individuals diagnosed with early-stage gastrointestinal tumours, precancerous lesions, or localised abnormalities within the gastrointestinal tract may be candidates for ESD. Patients who cannot undergo surgery due to underlying health conditions or those seeking less invasive treatment options often opt for ESD. The submucosa, or layer between the muscle wall and the lining of internal organs, can be affected by the tumours and lesions listed below, which can be treated using the ESD procedure:
- Barrett’s oesophagus
- Early-stage cancerous tumours or colon polyps, including stomach cancer, colorectal cancer, and oesophagal cancer.
- Tumours of the oesophagus, stomach, or colon that have not yet progressed to the deeper layers of the GI wall
For the removal of some growths, particularly those that are too big to be removed in one piece by conventional means or lack distinct boundaries, Endoscopic Suture Dissection (ESD) may be a more successful choice than Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR).
Before Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Before the procedure, patients undergo thorough assessments, including a medical history review, physical examination, and possibly imaging studies. You'll get detailed information on how to prepare for the endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure. You will need to fast for a few hours before the surgery if your gastroenterologist is treating your upper GI tract (stomach, oesophagus, or small intestine). You might need to have a bowel prep if they're treating your lower GI tract, which is your big intestine, which contains your colon and rectum. Bowel preparation, which involves cleansing the digestive tract, is crucial to ensure clear visibility during the procedure.
During Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Your gastroenterologist will do the ESD technique as follows:
- Patients receive sedation or anaesthesia to ensure comfort throughout the procedure.
- The endoscope is gently inserted through the mouth or anus, depending on the location of the abnormality.
- During the process, keep an eye on the images on a screen to prevent any injury to the surrounding tissue.
- The endoscopist identifies the lesion and marks its boundaries using special dyes.
- To remove the tumour or lesion from the muscular wall, inject a solution into the layer underneath it. By doing this, the procedure's injury to the surrounding tissue is reduced.
- Using specialized instruments, the targeted tissue's submucosal layer is precisely dissected and removed.
- Bleeding is managed during the procedure, and in some cases, the site may require closure using clips or other techniques.
- After removing the tissue from the body using an endoscope, send it to a lab so a pathologist may examine it.
- Typically, endoscopic submucosal dissection requires one to three hours to complete.
Recovery After Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Patients are monitored for a period post-ESD to watch for any complications. They will be kept under observation in a recovery room until the sedation wears off following the ESD operation. It may be determined whether the tumour has been totally eliminated by the pathologist by looking at tissue samples under a microscope. Patients may have some little soreness or discomfort in the location where the ESD was done throughout the healing phase. Painkillers obtained over-the-counter or by prescription, if necessary, can normally be used to treat this.
Initially, a liquid diet may be advised, gradually transitioning to soft foods. Medications to aid healing and prevent complications may be prescribed. Follow-up endoscopies are scheduled to monitor the treated area. In particular, if the patient is under intravenous sedation, they should refrain from using heavy machines. When under intravenous sedation, the patient should refrain from using heavy machinery. Similarly, it's best to refrain from attentive jobs like driving when tired and signing legal papers.
Advantages of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) offers several significant benefits, making it a preferred treatment option for certain gastrointestinal conditions:
- ESD is less invasive than traditional surgery, leading to reduced trauma, short hospital stays, and faster recovery for patients.
- ESD allows for precise dissection, enabling complete removal of larger lesions or abnormal tissues while minimising the risk of leaving any residual disease behind.
- By selectively removing abnormal tissues while preserving healthy tissues and organ function, ESD helps maintain the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Compared to conventional surgeries, ESD carries lower risks of complications such as infection, postoperative pain, and scarring, promoting a better overall patient experience.
Side Effects of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
While Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) is generally considered a safer option, as with any medical procedure, there are various potential side effects and risks associated with it:
- Immediate or delayed bleeding at the site of the resected tissue is a common side effect. Endoscopists manage this during the procedure and sometimes through additional interventions.
- There's a risk of creating a hole or perforation in the gastrointestinal tract during the dissection process. This is a serious complication that requires immediate attention.
- Patients might experience mild to moderate discomfort, throat irritation, or abdominal pain post-ESD, which typically resolves within a few days.
- Although uncommon, there is a small chance of infection at the surgery site, particularly if the gastrointestinal tract's protective lining is breached if there is a protracted healing period.
- In certain cases, scarring after ESD might cause narrowing (strictures) in the digestive tract, leading to difficulty in swallowing or bowel movements.
- Some rare Complications can include allergic reactions to anaesthesia, adverse reactions to medications used during the procedure, or uncommon complications related to the specific patient's health condition.
Difference Between Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) and Dissection (ESD)
While both EMR and ESD are minimally invasive procedures used for removing abnormal tissues in the gastrointestinal tract, the key differences lie in the technique and the size of lesions they can effectively manage.
- Endoscopic mucosal resection is used by gastroenterologists to treat tumours that develop in the mucosa, the inner membrane lining the gastrointestinal system. When a doctor does endoscopic mucosal excision, they remove the lesion with a metal loop while simultaneously injecting fluid beneath it. Tumours that grow deeper into your mucosa, as well as those that are on it, are treated with Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
- Every method has benefits and drawbacks of its own. EMR has a lengthy history of effectiveness for most precancerous lesions, is rather easy to implement, and requires few instruments. The major drawback of this therapy is that some individuals may need further surgery after receiving treatment with it. On the other hand, they may have recovered if ESD had been administered to them. One of the primary drawbacks of EMR is its high lesion recurrence rate, which can range from 15% to 20% and requires further therapy.
- ESD's primary benefit is that it enables thorough dissection of any kind of lesion, regardless of size. It does, however, need sophisticated endoscopic expertise and is more demanding technically than EMR. Comparing ESD to EMR, it is also a more involved process that has a greater perforation rate. Thankfully, endoscopy can effectively cure the majority of perforations produced by an ESD without requiring surgery.
Your gastroenterologist can remove tumours or abnormal growths from the surface layers of your digestive system using endoscopic submucosal dissection without cutting any skin. ESD will offer efficient treatment for early-stage gastrointestinal lesions as technology develops, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing the need for intrusive operations.
To Book an Appointment, call:
ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) for Achalasia Cardia
Peptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Treatment and How To Prevent
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.