-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Hepatitis C: Stages, Symptoms, Risks, Treatment and Prevention
Updated on 6 February 2024

Hepatitis C is a viral infection caused by the virus named Hepatitis C, which affects the liver and triggers an inflammatory response along with swelling. It can potentially trigger liver damage and even worsen the condition, leading to liver failure. Transmission of this viral pathogen is likely to occur by coming into contact with bodily fluids or the blood of an infected individual.
The hepatitis virus has a number of different strains, of which hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E are the most recognised and detected. These viruses differ in the method of transmission and the type of infections caused. People with hepatitis B infection will only get hepatitis D.
Understanding the Stages of Hepatitis C Infection
Infection by the hepatitis C virus occurs in different stages during which some people may likely experience some symptoms. However, these symptoms may be common or similar to other health conditions, which can make specific diagnoses improbable.
- Incubation period: This is the initial stage of infection when the virus first enters the body and reproduces to increase in number. The virus keeps replicating until the body's immune system recognizes the rise of infection and some symptoms begin appearing. This stage may last for a few weeks.
- Acute infection: The symptoms may not be noticeable from the very beginning as it is mostly limited to the liver. Only about a fifth of hepatitis C patients experience symptoms like fever and inflammation at this stage. This stage may last about three to six months.
- Chronic infection: A majority of people with hepatitis C infection don't experience any symptoms, which makes the detection much harder. This causes them to develop a long-term, chronic hepatitis C infection. At this stage, the liver remains constantly inflamed and swollen, which has a more damaging effect on the liver. It can eventually lead to scarring of the liver tissues.
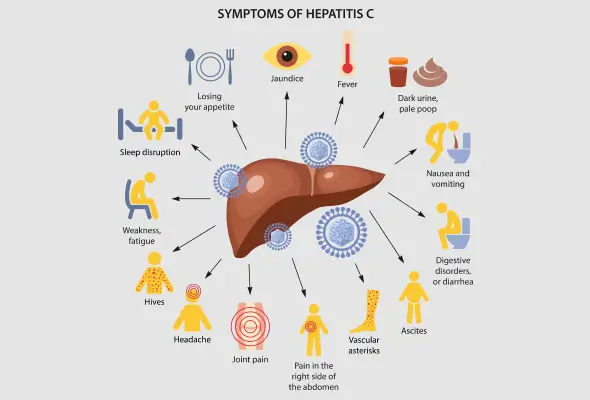
What are the Symptoms of Hepatitis C?
A small number of infected persons during the stage of acute infection may present flu-like symptoms, or there may be signs of liver damage like jaundice or abdominal pain. After a considerable period of time, they may begin noticing signs of liver failure as a result of chronic hepatitis C infection.
Acute infection stage:
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Body aches
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Jaundice
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Dark-coloured urine
- Lighter-coloured stools
Advanced infection stage:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Skin itchiness
- Swelling and fluid accumulation in the limbs and abdomen
- Bruising and bleeding easily
- Difficulty in recalling & fogginess of thoughts
How is Hepatitis C Transmitted?
Hepatitis C virus is primarily spread through exposure to the bodily fluids and blood of an infected individual. This is often a result of engaging in risky activities, including:
- Sharing drug use equipment like needles, syringes, or even tourniquets
- Getting tattooed using nonsterile instruments
- Unprotected intercourse with an infected individual
- Sharing or incorrectly disposing of toiletries like razors and nail clippers having some amount of blood on their surfaces
Hepatitis C– Who is at Risk?
Risk factors for Hepatitis C include:
- Having used drugs intravenously
- Having unprotected intercourse with multiple partners
- Having kidney dialysis
- Having an active HIV infection
- Being a healthcare professional working in an environment where they are exposed to instruments containing blood or handling blood samples
- Being an infected, pregnant mother, there is a risk of transmitting the hepatitis C virus to their unborn baby, especially if the baby is delivered vaginally
Treatment of Hepatitis C
Treatment of hepatitis C infection may be possible with the help of medications. The type of medication recommended depends upon the individual patient and varies based on their overall health condition and the strain of the virus affecting them.
Simply managing the symptoms of the hepatitis infection may not be enough to treat the condition, as most people are likely to experience some degree of liver damage or liver cirrhosis. These concerns also need to be addressed by evaluating liver health through elaborate diagnostic assessments of various parameters.
Liver Transplantation: Some patients may even be at the threshold of liver failure. The only possible cure for liver failure is liver transplantation. If a patient has been deemed fit for transplantation, they may need further evaluation of their liver health. Simultaneously, management and treatment of the existing hepatitis C would be necessary to prevent the spreading of the infection to the transplanted liver.
Preventing Hepatitis C
Although some strains of the hepatitis virus may be prevented by vaccination against it, vaccines against hepatitis C are not available. Therefore, it is advisable to exercise caution and avoid high-risk activities, especially sharing non-sterile needles or syringes, that may potentially lead to the contraction of the hepatitis C virus. It may also help in getting screening tests against the hepatitis C virus in case there is a doubt of prior exposure to blood.
Outlook
Thanks to newer medications being developed to treat hepatitis C, the prognosis of this infection is brighter. Long-term chronic infection may also be manageable and curable, sometimes within a matter of a few weeks. Although symptoms may not appear early on during the stages of infection, regular screening or testing with respect to minor symptoms may help prevent damage. Even when the infection has reached an advanced stage, there are ways to control and preserve the liver.
To Book an Appointment, call:
ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
5 Common Causes of Rectal Bleeding (Blood in Your Stool)
Belly Button Pain (Periumbilical Pain): Causes, Treatment and When to See a Doctor
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.