-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Anterior vs Posterior Placenta: What is the Difference?
Updated on 18 October 2023

Pregnancy is a remarkable journey, and understanding the nuances of your body's changes can provide valuable insights into your unique pregnancy experience. One of the key factors that can influence this experience is the location of the placenta in the uterus. In this blog, we will delve deep into the intricacies of anterior and posterior placentas, exploring their definitions, functions, and potential effects on both the mother and the growing baby. Whether you are an expectant mother seeking answers or simply curious about the wonders of pregnancy, join us as we unravel the mysteries of this remarkable aspect of prenatal development.
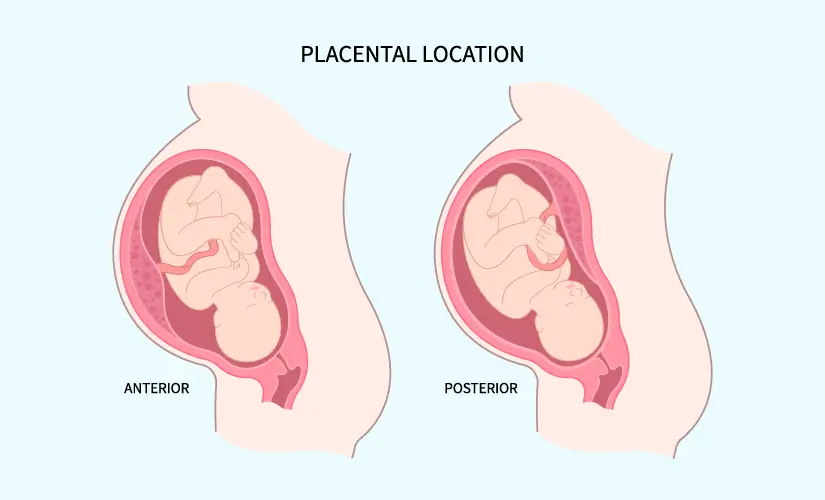
What is Anterior Placenta?
An anterior placenta refers to the placement of the placenta in the uterus during pregnancy. Specifically, it means that the placenta is attached to the front wall of the uterus, which is the side of the uterus that is closest to the abdominal wall of the pregnant woman. In other words, the anterior placenta is positioned between the baby and the mother's belly.
The placenta is an essential organ that develops during pregnancy and serves as the interface between the mother and the developing fetus. It provides oxygen, nutrients, and removes waste products from the baby's blood. The location of the placenta, whether it's anterior (front), posterior (back), or elsewhere in the uterus, can influence various aspects of the pregnancy experience, such as when a woman can feel fetal movements.
With an anterior placenta, some women may experience a delay in feeling their baby's movements compared to those with a posterior placenta because the placenta can act as a cushion and dampen sensations. However, it's important to note that the position of the placenta does not typically impact the overall health or development of the baby. Pregnant individuals with an anterior placenta should continue with regular prenatal care and monitoring as recommended by their healthcare provider.
What Is Posterior Placenta?
A posterior placenta, in the context of pregnancy, refers to the placement of the placenta in the uterus. Specifically, it means that the placenta is attached to the back wall of the uterus, which is the side of the uterus that is nearer to the mother's spine. In other words, the posterior placenta is positioned between the baby and the mother's back.
The placenta is a vital organ that forms during pregnancy and plays a crucial role in supporting the developing fetus. It serves as a bridge between the mother and the baby, providing oxygen, nutrients, and removing waste products from the baby's blood.
The location of the placenta, whether it's anterior (front), posterior (back), or elsewhere in the uterus, can influence various aspects of the pregnancy experience. In the case of a posterior placenta, some women may feel fetal movements earlier and more distinctly compared to those with an anterior placenta because there is less tissue between the baby's movements and the mother's abdominal wall.
It's important to note that while the position of the placenta can affect certain aspects of the pregnancy experience, it does not typically impact the overall health or development of the baby. Pregnant individuals with a posterior placenta should continue with regular prenatal care and monitoring as recommended by their healthcare providers
Key Differences Between Anterior and Posterior Placenta
The location of the placenta in the uterus, whether anterior or posterior, can impact various aspects of pregnancy. Here are the key differences between anterior and posterior placenta:
|
|
Anterior Placenta |
Posterior Placenta |
|
Placement in the Uterus |
Attached to the front wall of the uterus, between the baby and the mother's abdominal wall.
|
Attached to the back wall of the uterus, nearer to the mother's spine.
|
|
Fetal Movements |
The placenta may act as a cushion, dampening fetal movements, so some women may feel movements later or less distinctly.
|
Fetal movements are often felt earlier and more distinctly since there is less tissue between the baby's movements and the mother's abdominal wall.
|
|
Sensations During Pregnancy
|
Pregnant individuals with an anterior placenta may experience less sensation or pressure in the front of the abdomen but may feel more movements along the sides.
|
Sensations of the baby's movements and pressure may be more noticeable in the front of the abdomen.
|
|
Ultrasound Imaging |
In some cases, an anterior placenta can make it slightly more challenging to obtain clear ultrasound images, especially early in pregnancy, due to its location at the front of the uterus.
|
Ultrasound imaging is often easier and provides clearer views of the fetus with a posterior placenta.
|
|
Effect on Labor and Delivery
|
The position of the placenta generally does not significantly affect labor or delivery outcomes.
|
Similarly, the position of the placenta typically does not have a significant impact on labor and delivery, although it may affect the sensations experienced during contractions.
|
|
Overall Health and Development |
The location of the placenta does not typically impact the overall health or development of the baby. It primarily affects the perception of fetal movements. |
Like an anterior placenta, a posterior placenta does not generally impact the baby's health or development. It may result in more noticeable fetal movements.
|
It's important to remember that the position of the placenta is just one factor in the complex process of pregnancy. Healthcare providers routinely monitor pregnancies and provide guidance based on individual circumstances, taking into account factors such as the placenta's location, the baby's growth, and the mother's overall health.
How Anterior Placenta can affect Pregnancy?
An anterior placenta is when the placenta attaches to the front wall of the uterus. While it's usually not a cause for concern, it can affect pregnancy in several ways:
- Fetal Movement Sensation: The placenta acts as a cushion between the baby and the mother’s abdominal wall, which can make it harder to feel fetal movements, especially in the early stages of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound Imaging: An anterior placenta can sometimes make it more challenging to get clear images of the baby during an ultrasound. However, experienced technicians and doctors can still monitor the baby’s development effectively.
- Monitoring the Baby: Because of the cushioning effect, healthcare providers may need to use different techniques to monitor the baby's heartbeat and movements during prenatal visits.
- Labor and Delivery: In most cases, an anterior placenta does not affect the delivery process. However, if it is low-lying (near the cervix), it might increase the risk of complications like placenta previa, which could necessitate a C-section delivery.
- Amniocentesis and Other Procedures: If any procedures like amniocentesis are needed, the location of the anterior placenta will be taken into account to avoid complications.
- Potential for Placental Abruption: Though rare, an anterior placenta may have a slightly increased risk of placental abruption (where the placenta detaches from the uterine wall before delivery), but this risk is generally low.
Risks associated with Anterior and Posterior Placenta
Both anterior and posterior placenta positions are common and usually normal during pregnancy. However, each position can have some risks and considerations:
- Anterior Placenta
- Fetal Movement: The placenta can cushion the baby’s movements, making it harder for the mother to feel kicks and movements, especially in early pregnancy.
- Ultrasound Imaging: It can sometimes make it more challenging to obtain clear ultrasound images, but experienced technicians can still monitor the baby effectively.
- Labor and Delivery: Usually does not affect delivery. However, if the placenta is low-lying (placenta previa), it may require a C-section.
- Amniocentesis: The position must be considered during procedures like amniocentesis to avoid complications.
- Potential for Placental Abruption: Slightly increased risk, though still rare. Placental abruption is when the placenta detaches from the uterine wall before delivery, which can be a serious condition.
- Posterior Placenta
- Labor and Delivery: Generally poses no special risks for labor and delivery. It typically doesn't affect the birthing process.
- Fetal Movement: Movements are often felt more clearly and earlier in pregnancy since there is less cushioning.
- Back Pain: Some women may experience more back pain as the pregnancy progresses because the baby's weight is more concentrated towards the back.
- Low-Lying Placenta: Similar to the anterior placenta, if the posterior placenta is low-lying, it could lead to placenta previa, necessitating a C-section.
- Placental Abruption: There is no increased risk specific to posterior placentas, but placental abruption can occur in any placental location.
Pros and Cons of both Anterior and Posterior Placenta
Here are the pros and cons of having an anterior or posterior placenta:
Anterior Placenta
- Pros:
- Normal and Common: An anterior placenta is a normal and common placental position.
- Cushioning Effect: It can provide extra cushioning for the baby, which might be beneficial in protecting the baby from external impacts.
- Cons:
- Fetal Movement: You might feel baby’s movements later and less intensely because the placenta acts as a cushion.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Sometimes it can be harder to get clear images of the baby during ultrasounds, although experienced technicians can manage it.
- Labor and Delivery: If the placenta is low-lying (placenta previa), it may require a C-section.
- Procedures: During procedures like amniocentesis, special care is needed to avoid complications.
Posterior Placenta
- Pros:
- Fetal Movement: Baby’s movements are often felt more clearly and earlier since there is less cushioning.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Easier to get clear images of the baby during ultrasounds.
- Cons:
- Back Pain: More likely to experience back pain as the pregnancy progresses because the baby’s weight is more towards the back.
- Labor and Delivery: Generally poses no special risks, but if the placenta is low-lying, it could require a C-section, similar to an anterior placenta.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between anterior and posterior placenta positions adds another layer of insight to the incredible journey of pregnancy. While these positions may affect the way you experience your baby's movements and certain aspects of prenatal care, it's essential to remember that both anterior and posterior placentas serve the vital role of nourishing and supporting your growing child.
The beauty of pregnancy lies in its uniqueness—no two experiences are the same. Whether you feel those early flutters with the presence of a posterior placenta or patiently await your baby's kicks with an anterior one, every moment is a part of your individual pregnancy story.
As you embark on this remarkable journey, embrace the knowledge that your healthcare provider is your greatest ally. They will ensure that both you and your baby receive the best care and attention, regardless of the placental position. Cherish every moment, and may your pregnancy be filled with health, joy, and the wonder of new life.
Faqs
1) Which placenta position is best for normal delivery?
The best placenta position for normal delivery is one that is high and away from the cervix. It doesn't matter if it is anterior (front) or posterior (back) as long as it doesn't block the cervix.
2) What are the benefits of an anterior placenta?
An anterior placenta provides extra cushioning between the baby and the mother's abdomen, which can help protect the baby from external impacts. It is a common and usually normal position.
3) Can you have an anterior and posterior placenta?
No, typically you can only have one placenta that attaches to either the front (anterior) or the back (posterior) of the uterus. In rare cases, a placenta can have two lobes and might seem to attach in both places, but this is uncommon.
4) Is a posterior placenta high risk?
No, a posterior placenta is not high risk. It is a normal position for the placenta. The risks are similar to any placental position, such as if the placenta is low-lying and blocks the cervix (placenta previa).
5) Which is better, anterior or posterior?
Neither anterior nor posterior is better. Both are normal and healthy positions. The important thing is that the placenta is not blocking the cervix and there are no other complications. Regular prenatal checkups help ensure both mother and baby are healthy.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
White Discharge Before Period: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Which Foods to Eat and Avoid During Your Period
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.