-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
HIV and AIDS: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Updated on 11 April 2023

Table of Content
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks the immune system, and over time, can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). AIDS is a condition that occurs when the immune system is severely damaged, leaving the body susceptible to opportunistic infections and cancers. In this blog, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatments of HIV and AIDS.
Symptoms:
In the early stages, many people do not experience any symptoms of HIV AIDS. However, some people may experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, and fatigue, which can occur within 2-4 weeks after exposure to the virus. As the virus progresses, symptoms may include swollen lymph nodes, weight loss, diarrhoea, and night sweats. In the later stages of HIV, when it has progressed to AIDS, symptoms may include persistent cough, shortness of breath, and recurring fever.
Many people who contract HIV may not experience any symptoms initially. The progression of HIV infection typically goes through several stages:
- Acute HIV infection (Stage 1): This stage develops over a few weeks to months after infection and may include flu-like symptoms. However, these symptoms are often mild and can be easily mistaken for other illnesses.
- Chronic or Asymptomatic HIV infection (Stage 2): During this stage, which can last for a decade or more, individuals often do not display any noticeable symptoms. They may feel perfectly healthy, but it's important to note that they can still transmit the virus to others.
- AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) (Stage 3): Without treatment, nearly all HIV-infected individuals eventually progress to AIDS. Some may develop AIDS relatively quickly after infection, while others can remain healthy for 10 to 20 years, known as long-term nonprogressors.
- People with AIDS have a severely weakened immune system due to the damage caused by HIV. This weakened immune system puts them at a high risk of contracting uncommon infections, known as opportunistic infections, which can affect various parts of the body. These infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protozoa. Additionally, individuals with AIDS are more susceptible to certain cancers, particularly lymphomas and a skin cancer called Kaposi sarcoma.
The symptoms associated with HIV and AIDS vary depending on the specific opportunistic infection and the affected body part. Common symptoms include:
- Lung infections, often lead to cough, fever, and breathing difficulties.
- Intestinal infections, which may result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and swallowing difficulties.
- Other general symptoms like weight loss, fever, night sweats, rashes, and swollen lymph glands may also be present.
Causes:
HIV is primarily transmitted through the exchange of certain bodily fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk. The most common mode of transmission is through sexual contact, particularly unprotected sex with an infected partner. Sharing needles or syringes with an infected person, receiving blood transfusions or organ transplants from an infected person, and mother-to-child transmission during childbirth or breastfeeding are also possible routes of transmission.
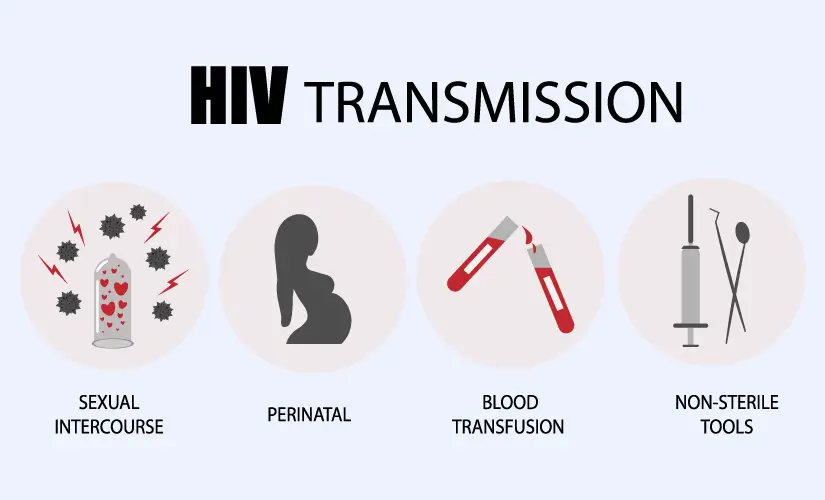
HIV is not transmitted through blood or organ donation processes. When people donate blood or organs, they do not come into direct contact with the recipients. Additionally, sterile needles and medical instruments are always used during these procedures.
Blood banks and organ donor programs conduct thorough screening of donors, blood, and tissues. Therefore, the chances of contracting HIV from blood transfusions, blood products, or organ or tissue transplants are extremely low.
Factors that increase the risk of HIV transmission include:
- Engaging in unprotected anal or vaginal intercourse, with receptive anal sex being the riskiest. Having multiple sexual partners also elevates the risk. Consistently using a new condom correctly during sexual activity significantly reduces this risk.
- Using drugs and sharing needles or syringes, which can expose individuals to contaminated blood or bodily fluids.
- Having a sexual partner who has HIV and is not taking HIV medications, as this increases the likelihood of transmission.
- Contracting a sexually transmitted disease (STD), which can facilitate the transmission of HIV.
Treatments:
While there is no cure for HIV or AIDS, there is treatment for HIV AIDS available that can help manage the virus and prevent the progression to AIDS. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the standard treatment for HIV. ART involves a combination of medications that suppress the virus, allowing the immune system to recover and preventing the progression to AIDS. ART has been shown to be highly effective, allowing people with HIV to live long and healthy lives.
In addition to ART, other treatments may be necessary to manage the symptoms and complications of HIV and AIDS. For example, medications to prevent and treat opportunistic infections, such as pneumonia and tuberculosis, may be prescribed. Supportive care, such as counselling and nutritional support, may also be recommended.
In the past, people with HIV would typically initiate antiretroviral treatment once their CD4 cell count dropped or when they experienced complications related to HIV infection. However, today, the recommended approach is to start HIV treatment for all individuals diagnosed with HIV, even if their CD4 cell count is within the normal range.
There are two main types of HIV treatment:
- Oral Medications (Pills): These are prescribed to individuals who are beginning HIV treatment.
- Injectable Medications (Shots): Some individuals may receive injectable medications if they have achieved an undetectable viral load (very low levels of HIV in the bloodstream) or have maintained viral suppression for at least three months. These injections can be administered monthly or every other month.
Regular blood tests are essential to monitor the viral load, which measures the amount of HIV virus in the bloodstream. The goal of treatment is to reduce the HIV virus in the blood to such low levels that it becomes undetectable on tests.
When treatment is initiated, and especially if CD4 cell counts had previously dropped, the CD4 count typically starts to rise gradually. As the immune system recovers, complications related to HIV infection often diminish or disappear.
How HIV spreads
To contract HIV, one must come into contact with infected blood, semen, or vaginal fluids, which can occur through various means:
- Sexual Contact: Infection can happen through vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse with an HIV-positive partner. The virus can enter the body through mouth sores or small tears that may develop during sexual activity.
- Needle Sharing: Sharing contaminated needles or syringes for drug injection poses a high risk for HIV transmission, as well as other infectious diseases like hepatitis.
- Blood Transfusions: Although rare in countries with rigorous blood screening, HIV transmission through blood transfusions can occur. The risk is higher in regions with limited screening resources.
- Mother-to-Child Transmission: Infected mothers can transmit the virus to their babies during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding. Timely treatment during pregnancy can substantially reduce this risk.
Prevention
Preventing the transmission of HIV is key to controlling the epidemic. There are several effective strategies for preventing HIV, including:
-
Practising safe sex by using condoms
-
Getting tested regularly for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
-
Avoiding sharing needles or syringes with others
-
Using only screened blood and organ products for transfusions or transplants
-
Treating pregnant women diagnosed with HIV to prevent mother-to-child transmission
In addition to these strategies, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a medication that can be taken by people at high risk of HIV to prevent infection.
Tests for HIV
- The ELISA test looks for antibodies in the blood or saliva. If the result is positive, it is usually verified by a follow-up test.
- Rapid Antibody Tests: These provide results faster than ELISA tests.
Nucleic Acid Test (NAT): This test looks for the virus directly in the blood by detecting its genetic material. It is used in the early stages of infection when antibodies may be ineffective.
Third-generation assays identify both HIV antibodies and antigens, allowing discovery earlier than antibody testing.
Home Test Kits: These kits allow people to test their own saliva or blood at home. Positive test findings must be confirmed by a healthcare expert.
Risk Factors of HIV
- Unprotected intercourse can increase the risk of HIV transmission.
- Sharing needles or syringes for injection, piercings can lead to HIV transmission if equipment is contaminated.
- HIV can be transmitted from an HIV-positive mother to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
- Healthcare workers or individuals exposed to blood or body fluids in work environment without protection are at risk.
- HIV can be transmitted through infected blood transfusions or organ transplants if the donor is HIV positive(although it is very rare).
- Having other STIs can increase the risk of contracting HIV as these infections can cause HIV transmission.
Understanding these risk factors and getting tested for HIV on a regular basis, especially after probable exposure or engaging in high-risk activities, is critical for early detection and timely treatment if infected. Prevention of HIV transmission requires safe intercourse techniques, the use of sterile needles, and the seeking of proper medical care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HIV and AIDS are serious conditions that can have significant health impacts. While there is no cure for these conditions, treatments are available that can help manage the virus and prevent the progression to AIDS. Prevention strategies, such as practising safe sex and avoiding sharing needles, are essential to controlling the spread of HIV. If you think you may have been exposed to HIV, getting tested and seeking medical care early can help improve outcomes and prevent the spread of the virus.
It is essential to contact a qualified doctor in case you have been exposed to any of the above and display any symptoms. Please visit www.carehospitals.com and fix up an appointment if you wish to seek medical help.
FAQs
1. What’s the difference between HIV and AIDS?
HIV and AIDS differ in that HIV is a virus that diminishes your immune system's strength, while AIDS is a condition that can develop due to HIV infection when your immune system is significantly compromised.
AIDS cannot occur unless you have been infected with HIV. Fortunately, with treatment that decelerates the virus's impact, not all individuals with HIV will develop AIDS. However, in the absence of treatment, nearly all HIV-positive individuals will eventually progress to AIDS.
2. How common is HIV?
New HIV infections have seen a reduction. In 2019, there were approximately 1.2 million individuals living with HIV in the United States. Alarmingly, about 13% of them are unaware of their HIV status, underscoring the significance of regular HIV testing.
3. What are the stages of HIV?
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) infection progresses through several stages, and the disease's severity varies at each stage. The stages of HIV infection are:
- Acute HIV Infection: Initial stage with flu-like symptoms or none.
- Clinical Latency (Chronic HIV Infection): Dormant phase with no or mild symptoms.
- Symptomatic HIV Infection: Some experience symptoms, including fever, diarrhea, and weight loss.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS): Advanced stage with severe immune system damage, leading to opportunistic infections and AIDS-defining illnesses.
4. What are AIDS-defining illnesses?
AIDS-defining illnesses are specific medical conditions that typically occur in individuals with advanced HIV infection (AIDS). These illnesses include severe opportunistic infections and certain cancers, such as Kaposi's sarcoma, Pneumocystis pneumonia, and invasive cervical cancer. Their presence is a key diagnostic criterion for AIDS.
5. What tests diagnose HIV?
Several tests are used to diagnose HIV infection:
- HIV Antibody Test: Detects antibodies produced by the immune system in response to HIV. Common types include ELISA and rapid antibody tests. If positive, further testing is done to confirm.
- Nucleic Acid Test (NAT): Detects the virus's genetic material directly. Used for early detection, and it's highly accurate.
- Antigen-Antibody Test (4th Generation or Combo Test): Detects both HIV antibodies and antigens (viral proteins), offering earlier detection than antibody tests alone.
- Home HIV Test Kits: Available for self-testing, they use oral fluid or blood samples and provide results at home.
- CD4 Cell Count: Measures immune system health and helps assess HIV progression.
- Viral Load Test: Measures the amount of HIV in the blood, assessing viral activity and treatment effectiveness.
- Western Blot Test: Used to confirm HIV infection when antibody tests are positive.
- Point-of-Care (POC) Tests: Rapid tests providing quick results, often used in clinics and outreach settings.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Tips to Prevent Water-Borne Diseases
Hypothermia – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.