-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Systolic vs Diastolic Blood Pressure: Know The Difference
Updated on 1 February 2024

Blood pressure is a key measure of heart health and is characterised by two essential components: systolic and diastolic. This article breaks down these measures, giving you important insights into your heart health. We'll cover the basics to make understanding blood pressure easy for everyone.
What is Systolic Blood Pressure?
Systolic blood pressure reflects the force exerted on arterial walls when the heart contracts during each heartbeat. Imagine your heart squeezing to pump blood throughout your body—that's the systolic phase. Represented as the top number in a blood pressure reading, a healthy systolic pressure is typically below 120 mm Hg. This measurement is crucial as it gauges the heart's effectiveness in circulating blood. Elevated systolic pressure may strain the arteries, potentially leading to cardiovascular issues. Monitoring and maintaining a healthy systolic blood pressure below 120 mm Hg is fundamental for overall heart health, ensuring the heart efficiently pumps blood to meet the body's demands.
What is Diastolic Blood Pressure?
Diastolic blood pressure, the second number in a blood pressure reading, indicates the pressure in arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. Measured in millimetres of mercury (mmHg), a normal diastolic pressure is typically below 80 mm Hg. This phase is crucial, revealing how well blood vessels relax and recoil after each heartbeat. In a reading like 120/80 mmHg, the diastolic pressure is 80. Consistently high diastolic pressure may signal health concerns, impacting the heart's ability to rest, potentially leading to complications. Regular monitoring of both systolic and diastolic pressures, alongside a healthy lifestyle, is essential for maintaining a balanced blood pressure and overall cardiovascular well-being. Regular check-ups provide valuable insights into blood pressure trends, guiding individuals toward proactive health management.
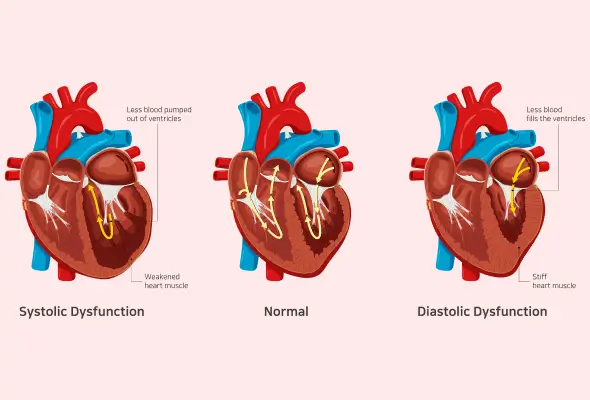
Systolic vs Diastolic Blood Pressure: The Difference
Here are the main differences between Systolic vs. Diastolic blood pressure:
- Definition: Systolic blood pressure (SBP) is the force when the heart contracts, pushing blood into arteries. Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) is the force when the heart relaxes between beats.
- Measurement: SBP is the higher number in blood pressure readings, while DBP is the lower number. For instance, in a reading of 120/80 mm Hg, 120 is SBP, and 80 is DBP.
- Heart's Work: SBP reflects the heart's effort to pump blood, while DBP shows the heart's rest phase.
- Artery Pressure: SBP measures pressure in arteries during heartbeats, while DBP measures pressure when the heart is at rest.
- Significance: High SBP may indicate artery stiffness or blockages, while high DBP can point towards issues with relaxation or narrowing of arteries.
- Risk Factors: High SBP is linked to heart strain, stroke, and kidney issues, while high DBP relates to kidney problems and risks of heart disease.
- Age Impact: SBP tends to rise with age, while DBP may decrease after the age of 50.
- Exercise Influence: Regular exercise can impact SBP more than DBP.
- Medication: Antihypertensive medications often target both SBP and DBP for effective blood pressure control.
- Healthy Range: A healthy blood pressure reading is typically around 120/80 mm Hg, but the range may vary based on health conditions and age. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals are essential for maintaining optimal blood pressure levels.
These factors can help you understand systolic blood pressure vs diastolic blood pressure with ease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, acquiring knowledge about both systolic and diastolic readings offers a comprehensive understanding of your heart's rhythm. A balanced reading of 120/80 mm Hg signifies optimal cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups, lifestyle choices that promote heart wellness, and an awareness of these figures empower you to confidently navigate through potential risks related to heart health.
FAQs
1. Why are systolic and diastolic readings important?
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings are crucial indicators of cardiovascular health. Systolic measures pressure when the heart contracts, while diastolic measures pressure when the heart is at rest. Monitoring these values helps assess the risk of heart disease, guiding preventive measures and healthcare decisions.
2. Is systolic more important than diastolic blood pressure?
No. Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure are important. Together, both values provide a comprehensive assessment of heart health.
3. What's a healthy blood pressure range?
A healthy blood pressure range is typically around 90/60 mm Hg to 120/80 mm Hg. The top number (systolic) measures the pressure during heartbeats, and the bottom number (diastolic) records the pressure between beats. Maintaining blood pressure within this range is crucial for cardiovascular health.
4. What does a high diastolic indicate?
A high diastolic blood pressure reading, the bottom number, typically above 90 mm Hg, indicates increased pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. This can suggest potential risks for heart disease, stroke, or other cardiovascular issues. It's crucial to monitor both systolic and diastolic readings for a comprehensive understanding of blood pressure health and consult with a healthcare professional for personalised advice.
5. Why is monitoring both important?
Monitoring is crucial for tracking changes and progress. By observing both, you can gain a comprehensive view, ensuring a holistic understanding of any situation and detecting any heart-related issues early on.
6. What is an alarming diastolic number?
An alarming diastolic number, the lower value in blood pressure readings, is typically considered anything above 90 mm Hg. This indicates higher pressure within the arteries during the heart's resting phase, posing a risk for cardiovascular issues. It's crucial to monitor blood pressure regularly and consult a healthcare professional for guidance if diastolic readings consistently exceed the normal range.
7. Is a diastolic reading of 55 too low?
A diastolic reading of 55 is generally considered within the normal range for blood pressure. However, individual health conditions and variations may influence what is considered normal for each person. It's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to get an assessment of your overall health and determine if the reading is appropriate for your specific situation.
To Book an Appointment, call:
ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Chronic Pain: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors and Treatment
How to Reduce Blood Sugar Level Immediately?
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.