-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
15 Healthy Foods Rich in Calcium
Updated on 3 October 2022

Calcium (Ca) plays an important role in maintaining bone health, including your teeth. Calcium also helps in maintaining the normal structure and function of heart muscles. Dairy products such as yoghurt, milk, and cheese are good sources of calcium, which primarily is needed to keep your bones healthy. In this article, we will discuss the top calcium-rich foods that are effective in treating calcium deficiency in your body.
Why You Need Calcium
Calcium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and supporting various bodily functions. It is well-known for its importance in building and maintaining strong bones and teeth, but its benefits go beyond skeletal health. Here are some compelling reasons why you need calcium:
- Bone Health: The primary and most well-known function of calcium is its role in building and maintaining strong bones and teeth. Calcium is a critical component of bone structure, providing strength and rigidity. Adequate calcium intake during childhood, adolescence, and early adulthood is crucial for reaching peak bone mass, which can help reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures later in life.
- Muscle Function: Calcium is involved in muscle contraction and relaxation. When a nerve stimulates a muscle, calcium is released, allowing the muscle fibers to contract. After the muscle contraction, calcium is pumped back into storage, leading to muscle relaxation. This process is essential for proper movement and function of the muscles, including the heart.
- Nerve Transmission: Calcium plays a crucial role in nerve transmission, allowing nerve cells to communicate effectively with each other and with other cells in the body. Proper nerve function is essential for coordination, sensory perception, and muscle control.
- Blood Clotting: Calcium is essential for the blood clotting process. When there is an injury or damage to blood vessels, calcium is released, initiating a series of reactions that lead to the formation of blood clots to stop bleeding. Without adequate calcium, blood clotting would be impaired, leading to excessive bleeding.
- Hormone Secretion: Calcium is involved in the secretion of various hormones, including insulin, which is essential for regulating blood sugar levels, and parathyroid hormone, which helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
- Cellular Signaling: Calcium serves as a secondary messenger in many cellular signaling pathways, helping to transmit signals within cells and between cells. These signaling processes are vital for various cellular activities, including cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Some research suggests that calcium may play a role in regulating blood pressure. Adequate calcium intake, combined with a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle, may help support healthy blood pressure levels.
15 Foods Rich in Calcium
Calcium is not only the most abundant mineral in the body, but it is also essential for proper body function. Dairy products and many other meals can help you maintain healthy calcium levels and prevent calcium insufficiency. Much of your bones and teeth are composed of calcium, which is also important for heart health, muscular function, and nerve signalling.
It is advised that most adults take at least 1,300 mg of calcium daily, while older persons, postmenopausal women, and adolescents need to take more calcium.
Even though dairy products—such as milk, cheese, and yoghurt—are particularly high in calcium, there are many calcium sources that don't involve dairy.
Calcium advantages in food:
- Seeds: Seeds such as celery, sesame, poppy, and chia seeds are very good sources of calcium. These seeds also offer healthy fats and proteins as well. Chia seeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and calcium. Thus, eating seeds can help to increase the calcium levels in the body.
- Cheese: Cheese is also an excellent source of calcium. Parmesan cheese is the best source of calcium in comparison to other cheeses. Our body can absorb calcium from dairy products easily as compared to plant sources. Dairy products have other health benefits such as lowering the risk of heart disease. Milk and yoghurt help in reducing the risk of metabolic syndrome.
- Yoghurt: Yoghurt is considered to be the best source of calcium. Yoghurt is also high in probiotics that help to improve the function of the immune system. Yoghurt also helps in maintaining a healthy heart and in the proper absorption of nutrients in the body. Greek yoghurt is a wonderful source to get essential proteins as well.
- Sardines and Canned Salmon: Salmon and Sardines are rich sources of calcium. These fish also provide high proteins and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients can help in improving heart function. These fish also provide nutrients that help to improve brain health and skin health.
- Beans and Lentils: Beans are rich in calcium, proteins, fibre, and micronutrients such as iron, folate, potassium, magnesium, zinc, and proteins. Some beans are also rich sources of calcium. Therefore, eating lentils and beans regularly can help increase calcium in the body.
- Almonds: Almonds have a high content of calcium and should be added to your daily diet. Almonds are also a rich source of fibre, proteins, and fats. These nuts are also a rich source of other nutrients such as vitamin E, manganese, and magnesium. Eating nuts can help in regulating blood pressure while maintaining calcium levels.
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Green leafy vegetables are very high in calcium. If you want to enhance the calcium levels in the blood you must eat spinach, collard greens, and kale. Thus, eating green leafy vegetables not only provides vitamins and minerals but also helps in boosting the immune system.
- Rhubarb: Rhubarb is an excellent source of vitamin K, calcium, and other vitamins and minerals. It also consists of fibre that helps in managing the function of the digestive system. Rhubarb is also rich in oxalates and helps in the quick absorption of calcium.
- Figs: Dried figs consist of high fibre and antioxidants. They also consist of high amounts of calcium. Figs also provide other nutrients such as vitamin K and potassium. These nutrients help in making your bones strong and healthy.
- Milk: Milk is considered one of the most important sources of calcium. Milk not only provides calcium but also provides Vitamin A and Vitamin D. Goat’s milk is a wonderful source of calcium. Milk can be absorbed easily and the calcium present in the milk can also be easily absorbed by the body.
- Tofu: Some tofu products are fortified with calcium during production, providing a plant-based calcium source for vegetarians and vegans.
- Fortified Foods: Certain cereals, fruit juices, and plant-based milk alternatives (like almond milk or soy milk) are often fortified with calcium to enhance their nutritional value.
- Broccoli: This vegetable contains a decent amount of calcium, along with other vitamins and antioxidants.
- Quinoa: This pseudocereal is not only a source of calcium but also provides complete protein and other minerals.
- Amaranth: Amaranth is a pseudo-grain that contains calcium and other essential nutrients.
Incorporating these foods that provide calcium into your diet can contribute to meeting your daily calcium needs, supporting bone health, muscle function, and overall well-being.
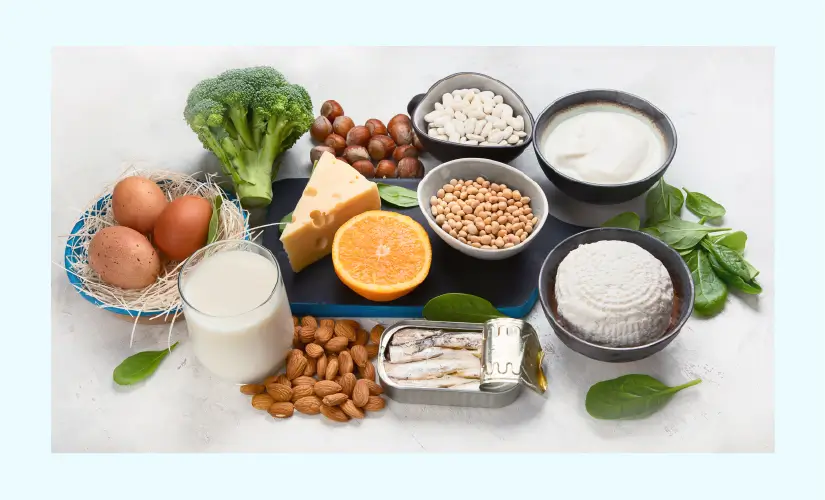

Fruits rich of calcium- also try including fruits rich of calcium in your diet such as:
- Apricots
- Kiwi
- Oranges
- Papaya
- Blackberries
- Pineapples
- Grapefruits
- Strawberries
- Litchy
- Guava
How Much Calcium Does Our Body Need?
The amount of calcium our body needs depends on factors like age and life stage.
- Adults (18-50 years): About 1000 milligrams (mg) per day.
- Women (51+ years) and Men (51-70 years): Around 1000-1200 mg per day.
- Women (71+ years) and Men (71+ years): Approximately 1200 mg per day.
Calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones, teeth, muscle function, nerve transmission, and blood clotting. It's found in various foods, including dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), leafy greens (kale, broccoli), nuts, seeds, and fortified plant-based milk alternatives. Adequate vitamin D intake is also important for proper calcium absorption.
Benefits of Calcium
Calcium is the most important mineral that makes your teeth and bones stronger. Our body has to work hard to maintain a normal calcium level in the body. If your blood has low levels of calcium and you do not eat foods rich in calcium then your bones will become weak. Thus, calcium is an important mineral needed for maintaining the good health of bones and teeth.
The principal function of vitamin D in calcium homeostasis is to increase calcium absorption from the intestine. The body needs vitamin D to absorb calcium. Without enough vitamin D, one can't form enough of the hormone calcitriol (known as the "active vitamin D"). This in turn leads to insufficient calcium absorption from the diet.
Osteoporosis is another condition that may result due to a deficiency of calcium in the body. It is a condition in which bones start losing calcium and the risk of fractures increases. Rickets is a disease that occurs in children due to a deficiency of calcium. It causes deformities of bones and there is delayed bone growth.
In conclusion, we have seen that a calcium-deficient person can face some severe complications. Therefore, it is wise to have the proper intake of calcium-rich food by adding them to your daily meals. You can also consult your doctor or dietician from the best hospital for dietetics & nutrition in Hyderabad for expert advice on calcium intake and avoiding its deficiency.
Calcium Dosage
|
Age Group |
Daily Calcium Requirement (RDA) |
|
0-6 months |
200 milligrams/day |
|
7-12 months |
260 milligrams/day |
|
1-3 years |
700 milligrams/day |
|
4-8 years |
1,000 milligrams/day |
|
9-18 years |
1,300 milligrams/day |
|
19-50 years |
1,000 milligrams/day |
|
51-70 years (Women) |
1,200 milligrams/day |
|
51-70 years (Men) |
1,000 milligrams/day |
|
70+ years |
1,200 milligrams/day |
Risks Associated with Calcium
- Side Effects: At standard doses, calcium supplements might result in bloating, gas, and constipation. Excessive calcium intake can potentially lead to the formation of kidney stones. Some research suggests a potential increased risk of heart attacks and strokes when taking calcium supplements alongside a high-calcium diet, but more research is needed to confirm this.
- Interactions: When regularly taking prescription or over-the-counter medications, consult your doctor about the safety of using calcium supplements. Calcium may interact with drugs for heart disease, diabetes, epilepsy, and other conditions. Vitamin D in high doses can elevate calcium levels dangerously, and excessive calcium intake may hinder the absorption of minerals like iron and zinc. To avoid interactions, it's generally recommended to take calcium supplements 1 to 2 hours apart from other medications or supplements.
- Other Calcium Forms: There is no substantiated evidence supporting the claim that products like "coral calcium" are superior to regular calcium. Additionally, coral calcium products may contain unsafe levels of lead.
- Risks: If you have kidney disease, heart issues, sarcoidosis, or bone tumors, consult your doctor before considering calcium supplements.
- Overdose: Elevated levels of calcium in the bloodstream can result in nausea, dry mouth, abdominal pain, irregular heartbeat, confusion, and, in extreme cases, death.
How Calcium Deficiency Affects Your Health?
Most of the calcium in your body is stored in your bones and teeth, with a smaller amount circulating in your blood and tissues.
Your body carefully regulates blood calcium levels. If the level drops due to insufficient calcium intake, your bones will release calcium to compensate.
Over time, this can weaken bones and lead to:
- Osteoporosis: Common in older adults, this condition involves a loss of bone density and a higher risk of fractures. Symptoms usually don’t appear until a fracture occurs.
- Rickets: A childhood disease that causes skeletal deformities and stunted growth, often due to vitamin D deficiency but can also be caused by low calcium.
How to know if you have calcium deficiency?
You might have a calcium deficiency if you experience:
- Muscle cramps or spasms (especially in your legs).
- Tingling or numbness in your fingers or around your mouth.
- Weak, brittle nails or hair loss.
- Fatigue and weakness that doesn’t go away.
- Bone pain or frequent fractures.
When to take calcium supplements?
You should take calcium supplements if:
- Your diet lacks calcium-rich foods like dairy, leafy greens, or fortified foods.
- You're pregnant or breastfeeding and need extra calcium.
- You're over 50 or post-menopause to help prevent bone loss.
- You have low bone density or osteoporosis.
- Your doctor recommends it due to specific medical conditions.
FAQ's
1. How do I get the most calcium? What foods are the best?
The most efficient way to obtain calcium is by incorporating a variety of calcium-rich foods into your diet. Some of the best sources of calcium include dairy products like milk, cheese, and yoghurt, as they are rich in readily absorbable calcium. Additionally, dark leafy greens such as kale and spinach, calcium-fortified plant-based milk alternatives, canned fish with edible bones like sardines, and tofu are excellent choices. Consuming a mix of these foods ensures a diverse intake of calcium, supporting overall bone health and fulfilling daily calcium requirements.
2. How can I get 1000 calcium a day?.
Achieving a daily calcium intake of 1000 milligrams can be accomplished by including various calcium-rich foods in your diet. Consuming three servings of dairy (such as milk, yogurt, or cheese), incorporating leafy greens, fortified foods, and sources like tofu, almonds, and canned fish with bones throughout your meals and snacks helps reach this target and supports overall bone health.
3. Is milk rich in calcium?
Yes, milk is a rich source of calcium. One cup of milk typically contains around 300 milligrams of calcium, making it an excellent and readily absorbable dietary source of this mineral. Additionally, milk provides other essential nutrients like protein, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to overall bone health and supporting various bodily functions.
4. Why is calcium important for the body?
Calcium is crucial for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth, supporting muscle function, nerve transmission, and blood clotting.
5. Are there non-dairy sources of calcium?
Yes, there are plenty of non-dairy sources of calcium, such as leafy green vegetables (like kale and bok choy), nuts and seeds (like almonds and chia seeds), tofu, and fortified plant-based milk.
6. How much calcium do I need daily?
The daily calcium needs vary by age and gender. For most adults, it's about 1,000 mg per day. Women over 50 and everyone over 70 need about 1,200 mg per day.
7. Is spinach a good source of calcium?
Spinach contains calcium, but it also has oxalates, which can inhibit calcium absorption. So, while it's a source, it's not the most efficient one.
8. Are there any risks associated with consuming too much calcium?
Yes, consuming too much calcium can lead to health issues like kidney stones, constipation, and impaired absorption of other essential minerals.
9. Is apples rich in calcium?
No, apples are not a significant source of calcium. They are more known for their fiber and vitamin content.
10. What happens when you don't get enough calcium?
A calcium deficiency can lead to weakened bones (osteoporosis), increased risk of fractures, muscle cramps, and, in severe cases, numbness or tingling in the fingers.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (38)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Common Mistakes That Damage Our Immune System
Iron-Rich Foods: 9 Foods Packed With Iron
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
6 February 2026
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
6 February 2026
Read More
-

Pulmonary Stenosis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatments
6 February 2026
Read More
-

Difference between Angioplasty and Angiography
6 February 2026
Read More
-

Hemoptysis (Coughing Up Blood): Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
2 February 2026
Read More
-

Leg Weakness: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
9 January 2026
Read More
-

Back Pain After C-Section: Causes and Home Remedies
9 January 2026
Read More
-

Belly Button Pain (Periumbilical Pain): Causes, Treatment and When to See a Doctor
9 January 2026
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.